Integrative Analyses of Circulating Proteins and Metabolites Reveal Sex Differences in the Associations with Cardiac Function among DCM Patients
- PMID: 38999939
- PMCID: PMC11241450
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136827
Integrative Analyses of Circulating Proteins and Metabolites Reveal Sex Differences in the Associations with Cardiac Function among DCM Patients
Abstract
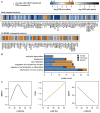
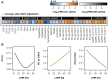
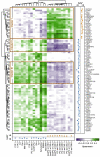
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is characterized by reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left or biventricular dilatation. We evaluated sex-specific associations of circulating proteins and metabolites with structural and functional heart parameters in DCM. Plasma samples (297 men, 71 women) were analyzed for proteins using Olink assays (targeted analysis) or LC-MS/MS (untargeted analysis), and for metabolites using LC MS/MS (Biocrates AbsoluteIDQ p180 Kit). Associations of proteins (n = 571) or metabolites (n = 163) with LVEF, measured left ventricular end diastolic diameter (LVEDDmeasured), and the dilation percentage of LVEDD from the norm (LVEDDacc. to HENRY) were examined in combined and sex-specific regression models. To disclose protein-metabolite relations, correlation analyses were performed. Associations between proteins, metabolites and LVEF were restricted to men, while associations with LVEDD were absent in both sexes. Significant metabolites were validated in a second independent DCM cohort (93 men). Integrative analyses demonstrated close relations between altered proteins and metabolites involved in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction with declining LVEF, with kynurenine as the most prominent finding. In DCM, the loss of cardiac function was reflected by circulating proteins and metabolites with sex-specific differences. Our integrative approach demonstrated that concurrently assessing specific proteins and metabolites might help us to gain insights into the alterations associated with DCM.
Keywords: Biocrates; DCM; LC MS/MS; OLINK; correlation; metabolomics; phenotype association; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arbelo E., Protonotarios A., Gimeno J.R., Arbustini E., Barriales-Villa R., Basso C., Bezzina C.R., Biagini E., Blom N.A., de Boer R.A., et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiomyopathies. Eur. Heart J. 2023;44:3503–3626. - PubMed
-
- Pinto Y.M., Elliott P.M., Arbustini E., Adler Y., Anastasakis A., Böhm M., Duboc D., Gimeno J., De Groote P., Imazio M., et al. Proposal for a revised definition of dilated cardiomyopathy, hypokinetic non-dilated cardiomyopathy, and its implications for clinical practice: A position statement of the ESC working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:1850–1858. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv727. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seferović P.M., Polovina M., Bauersachs J., Arad M., Ben Gal T., Lund L.H., Felix S.B., Arbustini E., Caforio A.L.P., Farmakis D., et al. Heart failure in cardiomyopathies: A position paper from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019;21:553–576. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1461. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

