WRKY Transcription Factor Responses and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses in Plants
- PMID: 38999954
- PMCID: PMC11241455
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136845
WRKY Transcription Factor Responses and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses in Plants
Abstract
Plants are subjected to abiotic stresses throughout their developmental period. Abiotic stresses include drought, salt, heat, cold, heavy metals, nutritional elements, and oxidative stresses. Improving plant responses to various environmental stresses is critical for plant survival and perpetuation. WRKY transcription factors have special structures (WRKY structural domains), which enable the WRKY transcription factors to have different transcriptional regulatory functions. WRKY transcription factors can not only regulate abiotic stress responses and plant growth and development by regulating phytohormone signalling pathways but also promote or suppress the expression of downstream genes by binding to the W-box [TGACCA/TGACCT] in the promoters of their target genes. In addition, WRKY transcription factors not only interact with other families of transcription factors to regulate plant defence responses to abiotic stresses but also self-regulate by recognising and binding to W-boxes in their own target genes to regulate their defence responses to abiotic stresses. However, in recent years, research reviews on the regulatory roles of WRKY transcription factors in higher plants have been scarce and shallow. In this review, we focus on the structure and classification of WRKY transcription factors, as well as the identification of their downstream target genes and molecular mechanisms involved in the response to abiotic stresses, which can improve the tolerance ability of plants under abiotic stress, and we also look forward to their future research directions, with a view of providing theoretical support for the genetic improvement of crop abiotic stress tolerance.
Keywords: WRKY transcription factor; abiotic stress response and tolerance; plant growth and development; target gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
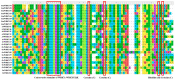
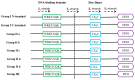
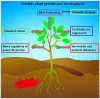
Similar articles
-
The physiological and molecular mechanisms of WRKY transcription factors regulating drought tolerance: A review.Gene. 2025 Feb 20;938:149176. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.149176. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39694344 Review.
-
Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors in Casuarina equisetifolia and the function analysis of CeqWRKY11 in response to NaCl/NaHCO3 stresses.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 8;24(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04889-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38714947 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factors under abiotic stresses in Carthamus tinctorius L.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 21;25(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06079-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39838282 Free PMC article.
-
The WRKY transcription factors in the diploid woodland strawberry Fragaria vesca: Identification and expression analysis under biotic and abiotic stresses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016 Aug;105:129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.014. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27105420
-
WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses.J Integr Plant Biol. 2017 Feb;59(2):86-101. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12513. J Integr Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 27995748 Review.
Cited by
-
CtWRKY41 Transcription Factor from Cynanchum thesioides Mediates Salt Stress Resistance and Controls Flowering Time.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jun 4;14(11):1716. doi: 10.3390/plants14111716. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508390 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of biological nitrogen fixation traits in mini-core cowpea germplasm.PLoS One. 2025 May 9;20(5):e0322203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322203. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40343950 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Leaves from Two Maize Hybrids Under Heat Stress During the Early Generative Stage.Genes (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;16(5):480. doi: 10.3390/genes16050480. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428302 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Expression Profiles of Identified WRKY Genes in Barley Landraces Under Cold Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 19;26(14):6948. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146948. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725197 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, evolution, and roles of MYB transcription factors proteins in secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways and abiotic stresses responses in plants: a comprehensive review.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jul 31;16:1626844. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1626844. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40822724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thudi M., Palakurthi R., Schnable J.C., Chitikineni A., Dreisigacker S., Mace E., Srivastava R.K., Satyavathi C.T., Odeny D., Tiwari V.K., et al. Genomic resources in plant breeding for sustainable agriculture. J. Plant Physiol. 2021;257:153351. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2020.153351. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

