Impaired Tertiary Dentin Secretion after Shallow Injury in Tgfbr2-Deficient Dental Pulp Cells Is Rescued by Extended CGRP Signaling
- PMID: 38999956
- PMCID: PMC11241056
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136847
Impaired Tertiary Dentin Secretion after Shallow Injury in Tgfbr2-Deficient Dental Pulp Cells Is Rescued by Extended CGRP Signaling
Abstract
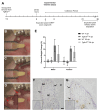
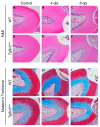
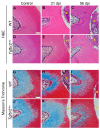
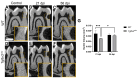
The transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) superfamily is a master regulator of development, adult homeostasis, and wound repair. Dysregulated TGFβ signaling can lead to cancer, fibrosis, and musculoskeletal malformations. We previously demonstrated that TGFβ receptor 2 (Tgfbr2) signaling regulates odontoblast differentiation, dentin mineralization, root elongation, and sensory innervation during tooth development. Sensory innervation also modulates the homeostasis and repair response in adult teeth. We hypothesized that Tgfbr2 regulates the neuro-pulpal responses to dentin injury. To test this, we performed a shallow dentin injury with a timed deletion of Tgfbr2 in the dental pulp mesenchyme of mice and analyzed the levels of tertiary dentin and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) axon sprouting. Microcomputed tomography imaging and histology indicated lower dentin volume in Tgfbr2cko M1s compared to WT M1s 21 days post-injury, but the volume was comparable by day 56. Immunofluorescent imaging of peptidergic afferents demonstrated that the duration of axon sprouting was longer in injured Tgfbr2cko compared to WT M1s. Thus, CGRP+ sensory afferents may provide Tgfbr2-deficient odontoblasts with compensatory signals for healing. Harnessing these neuro-pulpal signals has the potential to guide the development of treatments for enhanced dental healing and to help patients with TGFβ-related diseases.
Keywords: calcitonin gene-related peptide; dental pulp cells; fibrosis; neuropeptide; pulp biology; tertiary dentin; transforming growth factor beta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tgfbr2 in Dental Pulp Cells Guides Neurite Outgrowth in Developing Teeth.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 21;10:834815. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.834815. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35265620 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Tgfbr2 in Osterix-Cre expressing dental mesenchyme disrupts molar root formation.Dev Biol. 2013 Oct 1;382(1):27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23933490 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Tgfbr2 in odontoblasts leads to aberrant pulp calcification.J Dent Res. 2015 Jun;94(6):828-35. doi: 10.1177/0022034515577427. Epub 2015 Mar 12. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25818583
-
Odontoblasts: Specialized hard-tissue-forming cells in the dentin-pulp complex.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2016 Jul;56(4):144-53. doi: 10.1111/cga.12169. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2016. PMID: 27131345 Review.
-
Molecular regulation of odontoblast activity under dentin injury.Adv Dent Res. 2001 Aug;15:46-50. doi: 10.1177/08959374010150011201. Adv Dent Res. 2001. PMID: 12640739 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensory innervation of rat molar root pulp and dentin, apex, foramen, cellular cementum, vasculature and periodontium.Arch Oral Biol. 2025 Jun;174:106238. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2025.106238. Epub 2025 Mar 16. Arch Oral Biol. 2025. PMID: 40245584
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

