Role of Protein Phosphatases in Tumor Angiogenesis: Assessing PP1, PP2A, PP2B and PTPs Activity
- PMID: 38999976
- PMCID: PMC11241275
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136868
Role of Protein Phosphatases in Tumor Angiogenesis: Assessing PP1, PP2A, PP2B and PTPs Activity
Abstract
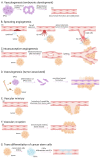
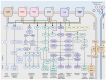
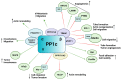
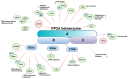
Tumor angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels to support tumor growth and metastasis, is a complex process regulated by a multitude of signaling pathways. Dysregulation of signaling pathways involving protein kinases has been extensively studied, but the role of protein phosphatases in angiogenesis within the tumor microenvironment remains less explored. However, among angiogenic pathways, protein phosphatases play critical roles in modulating signaling cascades. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the involvement of protein phosphatases in tumor angiogenesis, highlighting their diverse functions and mechanisms of action. Protein phosphatases are key regulators of cellular signaling pathways by catalyzing the dephosphorylation of proteins, thereby modulating their activity and function. This review aims to assess the activity of the protein tyrosine phosphatases and serine/threonine phosphatases. These phosphatases exert their effects on angiogenic signaling pathways through various mechanisms, including direct dephosphorylation of angiogenic receptors and downstream signaling molecules. Moreover, protein phosphatases also crosstalk with other signaling pathways involved in angiogenesis, further emphasizing their significance in regulating tumor vascularization, including endothelial cell survival, sprouting, and vessel maturation. In conclusion, this review underscores the pivotal role of protein phosphatases in tumor angiogenesis and accentuate their potential as therapeutic targets for anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer.
Keywords: Ser/Thr phosphatases; Tyr phosphatases; endothelial cells; protein phosphatases; signaling pathways; tumor angiogenesis; tumor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

