Lipid Droplet-Mitochondria Contacts in Health and Disease
- PMID: 38999988
- PMCID: PMC11240910
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136878
Lipid Droplet-Mitochondria Contacts in Health and Disease
Abstract
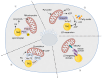
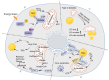
The orchestration of cellular metabolism and redox balance is a complex, multifaceted process crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Lipid droplets (LDs), once considered inert storage depots for neutral lipids, are now recognized as dynamic organelles critical in lipid metabolism and energy regulation. Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, play a central role in energy production, metabolic pathways, and redox signaling. The physical and functional contacts between LDs and mitochondria facilitate a direct transfer of lipids, primarily fatty acids, which are crucial for mitochondrial β-oxidation, thus influencing energy homeostasis and cellular health. This review highlights recent advances in understanding the mechanisms governing LD-mitochondria interactions and their regulation, drawing attention to proteins and pathways that mediate these contacts. We discuss the physiological relevance of these interactions, emphasizing their role in maintaining energy and redox balance within cells, and how these processes are critical in response to metabolic demands and stress conditions. Furthermore, we explore the pathological implications of dysregulated LD-mitochondria interactions, particularly in the context of metabolic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and their potential links to cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Conclusively, this review provides a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of LD-mitochondria interactions, underscoring their significance in cellular metabolism and suggesting future research directions that could unveil novel therapeutic targets for metabolic and degenerative diseases.
Keywords: disease; lipid droplet; metabolism; mitochondria; redox.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid droplet proteins and metabolic diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 May;1864(5 Pt B):1968-1983. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.07.019. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 28739173 Review.
-
Friend or Foe: Lipid Droplets as Organelles for Protein and Lipid Storage in Cellular Stress Response, Aging and Disease.Molecules. 2020 Oct 30;25(21):5053. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215053. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33143278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty Acid Trafficking Between Lipid Droplets and Mitochondria: An Emerging Perspective.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 10;21(5):1863-1873. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105361. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40083687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid droplets: Emerging therapeutic targets for age-related metabolic diseases.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Jun;108:102758. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102758. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 40300696 Review.
-
Lipid Droplets and Neurodegeneration.Neuroscience. 2024 Jun 21;549:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.04.014. Epub 2024 May 6. Neuroscience. 2024. PMID: 38718916 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrastructure analysis of mitochondria, lipid droplet and sarcoplasmic reticulum apposition in human heart failure.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 29:2025.01.29.635600. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.29.635600. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Jun 10;13:100461. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100461. PMID: 39975328 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Ultrastructure analysis of mitochondria, lipid droplet and sarcoplasmic reticulum apposition in human heart failure.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Jun 10;13:100461. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100461. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 40584838 Free PMC article.
-
Super-Resolution Microscopic Imaging of Lipid Droplets in Living Cells via Carbonized Polymer Dot-Based Polarity-Responsive Nanoprobe.ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024 Sep 6;4(5):593-598. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.4c00049. eCollection 2024 Oct 16. ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024. PMID: 39430970 Free PMC article.
-
Underneath the Gut-Brain Axis in IBD-Evidence of the Non-Obvious.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 12;25(22):12125. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212125. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From mitochondrial dysregulation to ferroptosis: Exploring new strategies and challenges in radioimmunotherapy (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Sep;67(3):76. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5781. Epub 2025 Aug 8. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40776761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mece O., Houbaert D., Sassano M.L., Durre T., Maes H., Schaaf M., More S., Ganne M., Garcia-Caballero M., Borri M., et al. Lipid droplet degradation by autophagy connects mitochondria metabolism to Prox1-driven expression of lymphatic genes and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:2760. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30490-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

