Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Comprehensive Regulation of Somatostatin DNA Vaccine in Goats
- PMID: 39000000
- PMCID: PMC11241611
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136888
Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Comprehensive Regulation of Somatostatin DNA Vaccine in Goats
Abstract
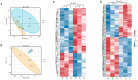
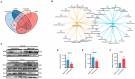
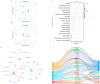
Somatostatin (SS) plays crucial regulatory roles in animal growth and reproduction by affecting the synthesis and secretion of growth hormone (GH). However, the mechanism by which SS regulates growth and development in goats is still unclear. In order to investigate the regulatory networks of the hypothalamus and pituitary in goats affected by SS DNA vaccines, in this study, we used a previously established oral attenuated Salmonella typhimurium SS DNA vaccine, X9241 (ptCS/2SS-asd), to treat wethers. We analyzed the protein changes in hypothalamic and pituitary tissues using a TMT-based proteomics approach. Additionally, we examined the metabolic profiles of the serum of control and immunized wethers through untargeted metabolomics using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Key signaling pathways were identified based on differentially expressed metabolites (DEMs) and differentially expressed proteins (DEPs). Furthermore, the effect of critical DEPs on signaling pathways was confirmed through Western blotting (WB) experiments, which elucidated the mechanism of active SS immunization in wethers. A proteomics analysis revealed that the expression of 58 proteins in the hypothalamus and 124 in the pituitary gland was significantly altered following SS vaccine treatment (fold change > 1.2 or < 0.83, p < 0.05). In the hypothalamus, many DEPs were associated with gene ontology (GO) terms related to neuronal signaling. In contrast, most DEPs were associated with metabolic pathways. In the pituitary gland, the DEPs were largely related to immune and nutrient metabolism functions, with significant enrichment in KEGG pathways, particularly those involving the metabolic pathway, sphingolipid signaling, and the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. A metabolomic analysis further showed that active SS immunization in wethers led to significant alterations in seven serum metabolites. Notably, the sphingolipid signaling pathway, secondary bile acid synthesis, sphingolipid metabolism, and lysine synthesis were significantly disrupted. SS vaccines induced marked changes in hypothalamic-pituitary proteins in wethers, facilitating alterations in their growth processes. This study not only provides insights into the mechanism of the SS gene in regulating GH secretion in wethers but also establishes a basis for hormone immunoregulation technology to enhance livestock production performance.
Keywords: DNA vaccine; dazu black goats; metabolomics; proteomics; somatostatin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunisation of the somatostatin gene alters hypothalamic-pituitary-liver gene expressions and enhances growth in Dazu black goats.Anim Biosci. 2024 Nov;37(11):1987-1999. doi: 10.5713/ab.24.0121. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Anim Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38938026 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive molecular characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma based on multi-omics analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 30;25(1):573. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13952-0. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40159482 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated proteomic and metabolomic profiling reveals novel insights on the inflammation and immune response in HFpEF.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 8;25(1):676. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10575-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38977985 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient Sensing Overrides Somatostatin and Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone to Control Pulsatile Growth Hormone Release.J Neuroendocrinol. 2015 Jul;27(7):577-87. doi: 10.1111/jne.12278. J Neuroendocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25808924 Review.
-
The regulation of GH secretion by sex steroids.Eur J Endocrinol. 2004 Nov;151 Suppl 3:U95-100. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.151u095. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15554893 Review.
Cited by
-
6-Methoxyflavone inhibits glycolytic energy metabolism in HeLa cells.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 17;25(1):719. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14133-9. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40247232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han Y., Na R., Jiang X., Wu J., Han Y., Zeng Y., Guangxin E., Liang A., Yang L., Zhao Y., et al. Effect of a novel somatostatin-14 DNA vaccine fused to tPA signal peptide and CpG adjuvant on goat lactation and milk composition. Small Rumin. Res. 2020;187:106107. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2020.106107. - DOI
-
- Meng J.Z., Li Q.Y., Xiao L.L., Liu W.C., Gao Z.J., Gong L., Lan X.Y., Wang S.L. Immunization against inhibin DNA vaccine as an alternative therapeutic for improving follicle development and reproductive performance in beef cattle. Front. Endocrinol. 2024;14:1275022. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1275022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NSFC, 32102544/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CYB23133/Chongqing Postgraduate Research Innovation Project
- No. CSTB2022TIAD-CUX0013/Chongqing Science and Technology Innovation Special Project
- S202210635213/Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduates of Southwest University
- SWU-XDJH202301/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

