Oleanolic Acid Dimers with Potential Application in Medicine-Design, Synthesis, Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity
- PMID: 39000101
- PMCID: PMC11241395
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136989
Oleanolic Acid Dimers with Potential Application in Medicine-Design, Synthesis, Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
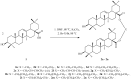
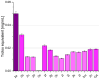
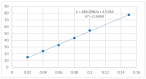
The present work aimed to obtain a set of oleanolic acid derivatives with a high level of cytotoxic and antioxidant activities and a low level of toxicity by applying an economical method. Oleanolic acid was alkylated with α,ω-dihalogenoalkane/α,ω-dihalogenoalkene to obtain 14 derivatives of dimer structure. All of the newly obtained compounds were subjected to QSAR computational analysis to evaluate the probability of the occurrence of different types of pharmacological activities depending on the structure of the analysed compound. All dimers were tested for cytotoxicity activity and antioxidant potential. The cytotoxicity was tested on the SKBR-3, SKOV-3, PC-3, and U-87 cancer cell lines with the application of the MTT assay. The HDF cell line was applied to evaluate the tested compounds' Selectivity Index. The antioxidant test was performed with a DPPH assay. Almost all triterpene dimers showed a high level of cytotoxic activity towards selected cancer cell lines, with an IC50 value below 10 µM. The synthesised derivatives of oleanolic acid exhibited varying degrees of antioxidant activity, surpassing that of the natural compound in several instances. Employing the DPPH assay, compounds 2a, 2b, and 2f emerged as promising candidates, demonstrating significantly higher Trolox equivalents and highlighting their potential for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. Joining two oleanolic acid residues through their C-17 carboxyl group using α,ω-dihalogenoalkanes/α,ω-dihalogenoalkenes resulted in the synthesis of highly potent cytotoxic agents with favourable SIs and high levels of antioxidant activity.
Keywords: SAR; antioxidant activity; cytotoxic activity; oleanolic acid; oleanolic acid dimers; triterpene dimers; triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acetylation of Oleanolic Acid Dimers as a Method of Synthesis of Powerful Cytotoxic Agents.Molecules. 2024 Sep 10;29(18):4291. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184291. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339286 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Oleanolic Acid Dimers-Cytostatic and Antioxidant Activities, Molecular Docking, and ADMETox Profile.Molecules. 2024 Jul 31;29(15):3623. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153623. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125028 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanolic Acid Lactones as Effective Agents in the Combat with Cancers-Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity, SAR Analysis, Molecular Docking and ADMETox Profile.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4099. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094099. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362338 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanolic acid and related derivatives as medicinally important compounds.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2008 Dec;23(6):739-56. doi: 10.1080/14756360701633187. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18618318 Review.
-
Oleanolic acid.Phytochemistry. 2012 May;77:10-5. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.12.022. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Phytochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22377690 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the Pharmacological Properties of Triterpenes Through Acetylation: An Anticancer and Antioxidant Perspective.Molecules. 2025 Jun 19;30(12):2661. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122661. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572628 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanolic Acid: A Promising Antioxidant-Sources, Mechanisms of Action, Therapeutic Potential, and Enhancement of Bioactivity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 16;14(5):598. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050598. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylation of Oleanolic Acid Dimers as a Method of Synthesis of Powerful Cytotoxic Agents.Molecules. 2024 Sep 10;29(18):4291. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184291. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339286 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Oleanolic Acid Dimers-Cytostatic and Antioxidant Activities, Molecular Docking, and ADMETox Profile.Molecules. 2024 Jul 31;29(15):3623. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153623. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125028 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities, Minerals Element Profiling, and Identification of Bioactive Compounds by UPLC-HRMS Orbitrap in Four Aromatic and Medicinal Plants.Molecules. 2025 Mar 12;30(6):1279. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061279. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40142055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nirmala M.J., Samundeeswari A., Sankar P.D. Natural plant resources in anti-cancer therapy—A review. Res. Plant Biol. 2011;1:1–14.
-
- Roaa M.H., Shoker A. The Importance of the Major groups of Plants Secondary Metabolism Phenols, Alkaloids, and Terpenes. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020;7:354–358. doi: 10.31033/ijrasb.7.5.47. - DOI
-
- Yeung M.F. A review on the presence of oleanolic acid in natural products. Nat. Proda Med. 2009;2:77–290.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

