Paradoxical Psoriasis in Patients Receiving Therapy with Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors: Potential Pathogenic Mechanisms and the Role of Genetic Factors
- PMID: 39000125
- PMCID: PMC11241744
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137018
Paradoxical Psoriasis in Patients Receiving Therapy with Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors: Potential Pathogenic Mechanisms and the Role of Genetic Factors
Abstract
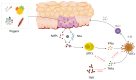
TNF inhibitors (TNFi) have revolutionized the therapeutic management of various chronic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Despite their known benefits, these therapies are related to paradoxical adverse effects (PAEs), including paradoxical psoriasis (PP). Although the underlying mechanism remains somewhat unclear, some theories suggest that genetic factors, particularly certain single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), may play an important role. The present review aimed to research and analyze recent findings regarding the pathomechanisms involved in the appearance of PP and the association between various genetic factors and PP in individuals treated with TNFi. We performed a literature search and found that certain genes (IL23R, TNF, FBXL19, CTLA4, SLC12A8, TAP1) are strongly associated with the occurrence of PP in pediatric and adult patients during therapy with TNFi. The identification of the specific SNPs involved in the appearance of PP and other PAEs in patients treated with TNFi for various diseases and in different populations may later favor the recognition of those patients at a high risk of developing such adverse effects and could guide personalized therapeutic strategies in future years.
Keywords: gene; genetic polymorphisms; genetic predisposition; paradoxical adverse effects; paradoxical psoriasis; tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gawdzik A., Ponikowska M., Jankowska-Konsur A., Woźniak Z., Maj J., Szepietowski J.C. Paradoxical Skin Reaction to Certolizumab, an Overlap of Pyoderma Gangrenosum and Psoriasis in a Young Woman Treated for Ankylosing Spondylitis: Case Report with Literature Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2020;10:869–879. doi: 10.1007/s13555-020-00398-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- García-Lagunar M.H., Gutiérrez-Cívicos M.R., García-Simón M.S., Conesa-Zamora P., Jiménez-Santos E., Cano-Vivar P., García-Márquez A., Muñoz-García I., Viney A. Reasons for discontinuation and adverse effects of TNFA inhibitors in a cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2016;51:388–393. doi: 10.1177/1060028016682330. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bucalo A., Rega F., Zangrilli A., Silvestri V., Valentini V., Scafetta G., Marraffa F., Grassi S., Rogante E., Piccolo A., et al. Paradoxical psoriasis induced by Anti-TNFA treatment: Evaluation of Disease-Specific Clinical and Genetic markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:7873. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217873. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Shea J.J., Gadina M., Siegel R.M. Cytokines and Cytokine Receptors. Elsevier eBooks; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. pp. 127–155.e1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

