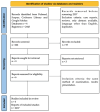
Difficulties in the Diagnostics and Treatment of Hashimoto's Encephalopathy-A Systematic and Critical Review
- PMID: 39000209
- PMCID: PMC11241003
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137101
Difficulties in the Diagnostics and Treatment of Hashimoto's Encephalopathy-A Systematic and Critical Review
Abstract
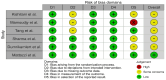
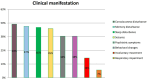
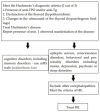
Hashimoto's encephalopathy (HE) has been a poorly understood disease. It has been described in all age group, yet, there is no specific HE marker. Additionally, the treatment data in the available studies are frequently divergent and contradictory. Therefore, the aim of our systematic and critical review is to evaluate the diagnosis and treatment of HE in view of the latest findings. The databases browsed comprised PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar as well as Cochrane Library, and the search strategy included controlled vocabulary and keywords. A total of 2443 manuscripts were found, published since the beginning of HE research until February 2024. In order to determine validity of the data collected from studies, bias assessment was performed using RoB 2 tool. Ultimately, six studies were included in our study. HE should be considered in the differential diagnosis in patients with psychiatric and neurological symptoms. According to our findings, negative thyroid peroxidase antibodies (anti-TPOs) may represent a valuable parameter in ruling out HE. Nonetheless, this result cannot be used to confirm HE. Furthermore, the proposed anti NH2-terminal-α-enolase (anti-NAE) is non-specific for HE. The effectiveness of glucocorticoid therapy is 60.94%, although relapse occurs in 31.67% of patients following the treatment. Our review emphasizes the significance of conducting further large-scale research and the need to take into account the potential genetic factor.
Keywords: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; anti-TPO; encephalopathy; steroid-responsive encephalopathy associated with autoimmune thyroiditis; steroidotheraphy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selenium supplementation for Hashimoto's thyroiditis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 6;2013(6):CD010223. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010223.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23744563 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Autoimmune Thyroid Disease in Patients with Down Syndrome-Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):29. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010029. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Turner Syndrome and the Thyroid Function-A Systematic and Critical Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;25(23):12937. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312937. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684648 Free PMC article.
-
Hashimoto's Encephalopathy: Clinical Features, Therapeutic Strategies, and Rehabilitation Approaches.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 17;13(3):726. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030726. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

