Identifying Key Genes Involved in Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Using Advanced RNA-Seq Analysis: A Methodological Approach with GLMQL and MAS
- PMID: 39000413
- PMCID: PMC11242629
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25137306
Identifying Key Genes Involved in Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Using Advanced RNA-Seq Analysis: A Methodological Approach with GLMQL and MAS
Abstract
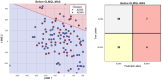
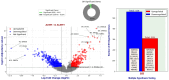
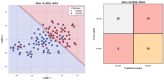
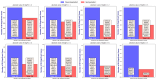
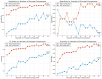
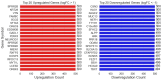
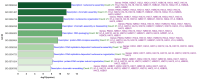
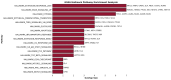
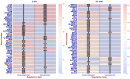
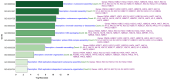
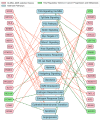
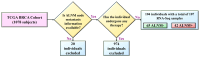
Our study aims to address the methodological challenges frequently encountered in RNA-Seq data analysis within cancer studies. Specifically, it enhances the identification of key genes involved in axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM) in breast cancer. We employ Generalized Linear Models with Quasi-Likelihood (GLMQLs) to manage the inherently discrete and overdispersed nature of RNA-Seq data, marking a significant improvement over conventional methods such as the t-test, which assumes a normal distribution and equal variances across samples. We utilize the Trimmed Mean of M-values (TMMs) method for normalization to address library-specific compositional differences effectively. Our study focuses on a distinct cohort of 104 untreated patients from the TCGA Breast Invasive Carcinoma (BRCA) dataset to maintain an untainted genetic profile, thereby providing more accurate insights into the genetic underpinnings of lymph node metastasis. This strategic selection paves the way for developing early intervention strategies and targeted therapies. Our analysis is exclusively dedicated to protein-coding genes, enriched by the Magnitude Altitude Scoring (MAS) system, which rigorously identifies key genes that could serve as predictors in developing an ALNM predictive model. Our novel approach has pinpointed several genes significantly linked to ALNM in breast cancer, offering vital insights into the molecular dynamics of cancer development and metastasis. These genes, including ERBB2, CCNA1, FOXC2, LEFTY2, VTN, ACKR3, and PTGS2, are involved in key processes like apoptosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis, response to hypoxia, and KRAS signaling pathways, which are crucial for tumor virulence and the spread of metastases. Moreover, the approach has also emphasized the importance of the small proline-rich protein family (SPRR), including SPRR2B, SPRR2E, and SPRR2D, recognized for their significant involvement in cancer-related pathways and their potential as therapeutic targets. Important transcripts such as H3C10, H1-2, PADI4, and others have been highlighted as critical in modulating the chromatin structure and gene expression, fundamental for the progression and spread of cancer.
Keywords: RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq); axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM); breast cancer; gene expression analysis; generalized linear models; quasi-likelihood F test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Negoita S., Chen H.S., Sanchez P.V., Sherman R.L., Henley S.J., Siegel R.L., Sung H., Scott S., Benard V.B., Kohler B.A., et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, part 2: Early assessment of the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on cancer diagnosis. Cancer. 2024;130:117–127. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. [(accessed on 10 January 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html.
-
- American Cancer Society. [(accessed on 10 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

