Enhancing Wound Recovery: A Self-Gelling Powder for Improved Hemostasis and Healing
- PMID: 39000650
- PMCID: PMC11244271
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16131795
Enhancing Wound Recovery: A Self-Gelling Powder for Improved Hemostasis and Healing
Abstract
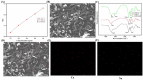
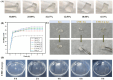
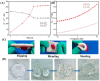
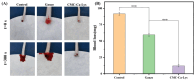
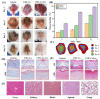
A novel self-gelatinizing powder was designed to accelerate wound healing through enhanced hemostasis and tissue recovery. Significantly, this research addresses the critical need for innovative wound management solutions by presenting a novel approach. Carboxymethylcellulose calcium (CMC-Ca) was synthesized using an ion exchange method, and lysine (Lys) was integrated through physical mixing to augment the material's functional characteristics. The prepared powder underwent comprehensive evaluation for its self-gelling capacity, gelation time, adhesion, swelling rate, coagulation efficiency, hemostatic effectiveness, and wound healing promotion. Results indicate that the self-gelatinizing powder exhibited remarkable water absorption capabilities, absorbing liquid up to 30 times its weight and achieving rapid coagulation within 3 min. The inclusion of Lys notably enhanced the powder's gel-forming properties. The gelation time was determined to be within 4 s using a rotational rheometer, with the powder rapidly forming a stable gel on the skin surface. Furthermore, in a mouse skin injury model, near-complete skin recovery was observed within 14 days, underscoring the powder's impressive self-healing attributes and promising application prospects in wound management.
Keywords: carboxymethylcellulose calcium; healing; hemostasis; lysine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

