Novel Optical Methodology Unveils the Impact of a Polymeric Pour-Point Depressant on the Phase Morphology of Waxy Crude Oils
- PMID: 39000788
- PMCID: PMC11243897
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16131933
Novel Optical Methodology Unveils the Impact of a Polymeric Pour-Point Depressant on the Phase Morphology of Waxy Crude Oils
Abstract
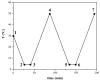
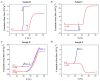
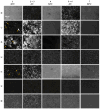
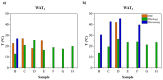
Crude oil, also known as petroleum, plays a crucial role in global economies, politics, and technological advancements due to its widespread applications in industrial organic chemistry. Despite environmental concerns, the dwindling supply of easily accessible oil reservoirs necessitates the exploration of unconventional resources, such as heavy and extra-heavy oils. These oils, characterized by high viscosity and complex composition, pose challenges in extraction, transportation, and refinement. With decreasing temperatures, heavy oils undergo phase changes, with transitions from Newtonian to non-Newtonian fluid behavior, leading to difficulties in transportation. Alternative methods, such as the use of polymeric pour-point depressants, help mitigate flowability issues by preventing wax precipitation. Understanding the properties of waxy crude oil, such as the wax appearance temperature (WAT), is crucial for effective mitigation strategies. The objective of this research is to determine the WATs of different types of waxy crude oils through a comparative analysis using advanced techniques such as cross-polar microscopy (CPM), standard rheology, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Disparities in WAT identified through different analytical methods highlight the potential of microscopy to enhance our understanding of complex fluid dynamics in real time in order to proactively identify and address crystallization issues in oilfields.
Keywords: flow assurance; phase morphology; polymeric pour point depressants; waxy crude oils.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Rosalia Ferraro and Sergio Caserta were employed by the company CEINGE Advanced Biotechnologies Franco Salvatore, and Author Salvatore Coppola was employed by the company Versalis S.p.A. (Eni). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vassiliou M.S. Historical Dictionary of the Petroleum Industry. Rowman & Littlefield; Lanham, MD, USA: 2018.
-
- Martínez-Palou R., Mosqueira M.d.L., Zapata-Rendón B., Mar-Juárez E., Bernal-Huicochea C., de la Cruz Clavel-López J., Aburto J. Transportation of heavy and extra-heavy crude oil by pipeline: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2011;75:274–282. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2010.11.020. - DOI
-
- Yadav V.G., Yadav G.D., Patankar S.C. The production of fuels and chemicals in the new world: Critical analysis of the choice between crude oil and biomass vis-à-vis sustainability and the environment. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy. 2020;22:1757–1774. doi: 10.1007/s10098-020-01945-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sena M.F.M.d., Rosa L.P., Szklo A. Will Venezuelan extra-heavy oil be a significant source of petroleum in the next decades? Energy Policy. 2013;61:51–59. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2013.05.101. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

