Robust Detection of Critical Events in the Context of Railway Security Based on Multimodal Sensor Data Fusion
- PMID: 39000897
- PMCID: PMC11244095
- DOI: 10.3390/s24134118
Robust Detection of Critical Events in the Context of Railway Security Based on Multimodal Sensor Data Fusion
Abstract
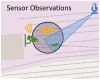
Effective security surveillance is crucial in the railway sector to prevent security incidents, including vandalism, trespassing, and sabotage. This paper discusses the challenges of maintaining seamless surveillance over extensive railway infrastructure, considering both technological advances and the growing risks posed by terrorist attacks. Based on previous research, this paper discusses the limitations of current surveillance methods, particularly in managing information overload and false alarms that result from integrating multiple sensor technologies. To address these issues, we propose a new fusion model that utilises Probabilistic Occupancy Maps (POMs) and Bayesian fusion techniques. The fusion model is evaluated on a comprehensive dataset comprising three use cases with a total of eight real life critical scenarios. We show that, with this model, the detection accuracy can be increased while simultaneously reducing the false alarms in railway security surveillance systems. This way, our approach aims to enhance situational awareness and reduce false alarms, thereby improving the effectiveness of railway security measures.
Keywords: multi-sensor fusion; sensor data fusion; surveillance of critical infrastructure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Andreas Haderer, Susanne Rechbauer and Sebastian Poltschak were employed by the company Joby Austria GmBH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Killen A., Coxon D.S., Napper D.R. A Review of the Literature on Mitigation Strategies for Vandalism in Rail Environments; Auckland, New Zealand. 2017. [(accessed on 9 May 2024)]. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:168167086.
-
- Grabušić S., Barić D. A Systematic Review of Railway Trespassing: Problems and Prevention Measures. Sustainability. 2023;15:13878. doi: 10.3390/su151813878. - DOI
-
- Fogaça J., Brandão T., Ferreira J.C. Deep Learning-Based Graffiti Detection: A Study Using Images from the Streets of Lisbon. Appl. Sci. 2023;13:2249. doi: 10.3390/app13042249. - DOI
-
- Cao Z., Qin Y., Xie Z., Liu Q., Zhang E., Wu Z., Yu Z. An effective railway intrusion detection method using dynamic intrusion region and lightweight neural network. Measurement. 2022;191:110564. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110564. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

