Combined PIVKA II and Vimentin-Guided EMT Tracking in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Combined Biomarker-Guided EMT Tracking in PDAC
- PMID: 39001424
- PMCID: PMC11240554
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16132362
Combined PIVKA II and Vimentin-Guided EMT Tracking in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Combined Biomarker-Guided EMT Tracking in PDAC
Abstract
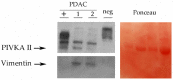
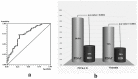
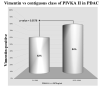
"Background/Aim": the current inability to diagnose Pancreatic Cancer Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) at an early stage strongly influences therapeutic strategies. Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence (PIVKA II) showed an accurate diagnostic performance for PDAC. Since circulating PIVKA II has been recently associated with pancreatic origin cells with Vimentin, an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) early activation marker, the aim of this study was to investigate in vivo the combination between the two proteins. "Materials and Methods": we assayed the presence of PIVKA II and Vimentin proteins by using different diagnostic methods. A total of 20 PDAC patients and 10 healthy donors were tested by Western Blot analysis; 74 PDAC patient and 46 healthy donors were assayed by ECLIA and Elisa. "Results": Western Blot analysis showed the concomitant expression of PIVKA II and Vimentin in PDAC patient sera. Immunometric assay performed on a larger cohort of patients demonstrated that 72% of PIVKA II-positive PDAC patients were Vimentin-positive. Additionally, in a group of PDAC patients with PIVKA II levels ≥2070 ng/mL, the percentage of Vimentin-positive subjects reached 84%. "Conclusion": the association between PIVKA II protein and the EMT suggests that this molecule could be considered a marker of the acquisition of an aggressive phenotype.
Keywords: EMT; PDAC; PIVKA II; Vimentin; biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have disclosed any financial or personal relationship with organizations that could potentially be perceived as influencing the described research.
Figures
References
-
- Ducreux M., Cuhna A.S., Caramella C., Hollebecque A., Burtin P., Goéré D., Seufferlein T., Haustermans K., Van Laethem J.L., Conroy T., et al. Cancer of the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26((Suppl. S5)):v56–v68. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv295. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murakawa M., Kawahara S., Takahashi D., Kamioka Y., Yamamoto N., Kobayashi S., Ueno M., Morimoto M., Sawazaki S., Tamagawa H., et al. Risk factors for early recurrence in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who underwent curative resection. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023;21:263. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03141-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

