Integrating Omics Data and AI for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
- PMID: 39001510
- PMCID: PMC11240413
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16132448
Integrating Omics Data and AI for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Abstract
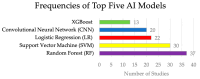
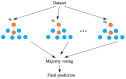
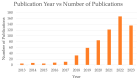
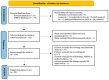
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death, making timely diagnosis and prognosis very important. Utilization of AI (artificial intelligence) enables providers to organize and process patient data in a way that can lead to better overall outcomes. This review paper aims to look at the varying uses of AI for diagnosis and prognosis and clinical utility. PubMed and EBSCO databases were utilized for finding publications from 1 January 2020 to 22 December 2023. Articles were collected using key search terms such as "artificial intelligence" and "machine learning." Included in the collection were studies of the application of AI in determining cancer diagnosis and prognosis using multi-omics data, radiomics, pathomics, and clinical and laboratory data. The resulting 89 studies were categorized into eight sections based on the type of data utilized and then further subdivided into two subsections focusing on cancer diagnosis and prognosis, respectively. Eight studies integrated more than one form of omics, namely genomics, transcriptomics, epigenomics, and proteomics. Incorporating AI into cancer diagnosis and prognosis alongside omics and clinical data represents a significant advancement. Given the considerable potential of AI in this domain, ongoing prospective studies are essential to enhance algorithm interpretability and to ensure safe clinical integration.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cancer; deep learning; machine learning; omics technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-omics based artificial intelligence for cancer research.Adv Cancer Res. 2024;163:303-356. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2024.06.005. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Adv Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39271266 Review.
-
Research and application of omics and artificial intelligence in cancer.Phys Med Biol. 2024 Oct 18;69(21). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad6951. Phys Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39079556 Review.
-
A review on deep learning applications in highly multiplexed tissue imaging data analysis.Front Bioinform. 2023 Jul 26;3:1159381. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1159381. eCollection 2023. Front Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37564726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning and multi-omics integration: advancing cardiovascular translational research and clinical practice.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 2;23(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06425-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40176068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung cancer multi-omics digital human avatars for integrating precision medicine into clinical practice: the LANTERN study.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 13;23(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10997-x. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37312079 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomics Studies on Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Glioblastoma: Where Do We Stand?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 10;25(18):9778. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189778. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraplaque haemorrhage quantification and molecular characterisation using attention based multiple instance learning.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 26:2025.03.04.25323316. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.04.25323316. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40093230 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
AI-Powered Insights into Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer: A Path Toward Precision Therapy.Iran J Pharm Res. 2025 May 25;24(1):e159954. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-159954. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2025. PMID: 40708930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the use of Radiomics and Pathomics for predicting the efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy in tumors.Transl Oncol. 2025 Aug;58:102435. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102435. Epub 2025 May 30. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40449473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and technologies in cancer epigenetics.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 7;14:1513654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1513654. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39839798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Copeland B. Alan Turing and the beginning of AI. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2024. [(accessed on 4 February 2024)]. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence/Alan-Turin....
-
- Samaras A., Bekiaridou A., Papazoglou A.S., Moysidis D.V., Tsoumakas G., Bamidis P., Tsigkas G., Lazaros G., Kassimis G., Fragakis N., et al. Artificial intelligence-based mining of electronic health record data to accelerate the digital transformation of the national cardiovascular ecosystem: Design protocol of the CardioMining study. BMJ Open. 2023;13:e068698. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068698. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

