Plasma Metabolome Signatures to Predict Responsiveness to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39001535
- PMCID: PMC11240312
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16132473
Plasma Metabolome Signatures to Predict Responsiveness to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) has arisen as a treatment option for breast cancer (BC). However, the response to NACT is still unpredictable and dependent on cancer subtype. Metabolomics is a tool for predicting biomarkers and chemotherapy response. We used plasma to verify metabolomic alterations in BC before NACT, relating to clinical data.
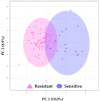
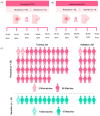
Methods: Liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was performed on pre-NACT plasma from patients with BC (n = 75). After data filtering, an SVM model for classification was built and validated with 75%/25% of the data, respectively.
Results: The model composed of 19 identified metabolites effectively predicted NACT response for training/validation sets with high sensitivity (95.4%/93.3%), specificity (91.6%/100.0%), and accuracy (94.6%/94.7%). In both sets, the panel correctly classified 95% of resistant and 94% of sensitive females. Most compounds identified by the model were lipids and amino acids and revealed pathway alterations related to chemoresistance.
Conclusion: We developed a model for predicting patient response to NACT. These metabolite panels allow clinical gain by building precision medicine strategies based on tumor stratification.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer biology; drug resistance; metabolomics; neoadjuvant chemotherapy response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum metabolomic profiling for predicting therapeutic response and toxicity in breast cancer neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a retrospective longitudinal study.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 6;27(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01956-w. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39762945 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting dynamic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a novel metabolomics approach.Mol Oncol. 2022 Jul;16(14):2658-2671. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13216. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35338693 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics by NMR Combined with Machine Learning to Predict Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response for Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;14(20):5055. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205055. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291837 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant therapy in hormone Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative breast cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2024 Feb;123:102669. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102669. Epub 2023 Dec 10. Cancer Treat Rev. 2024. PMID: 38141462 Review.
-
Radiological and Pathological Predictors of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer: A Brief Literature Review.Pathobiology. 2015 Sep;82(3-4):124-32. doi: 10.1159/000433582. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Pathobiology. 2015. PMID: 26330353 Review.
Cited by
-
Resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancers: a metabolic perspective.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 11;44(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03500-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40790759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From multi-omics to predictive biomarker: AI in tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1514977. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1514977. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39763649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Metabolic Biomarkers in Breast Cancer: A Literature Review.Ann Lab Med. 2025 May 1;45(3):229-246. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0482. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Ann Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 40091629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of serum metabolite biomarkers and metabolic reprogramming mechanisms to predict recurrence in cholangiocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 14;15(1):12782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97641-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40229491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torrisi R., Marrazzo E., Agostinetto E., De Sanctis R., Losurdo A., Masci G., Tinterri C., Santoro A. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative early breast cancer: When, why and what? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021;160:103280. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103280. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

