LncRNA ZFAS1 regulates ATIC transcription and promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 39001904
- PMCID: PMC11246283
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05877-1
LncRNA ZFAS1 regulates ATIC transcription and promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
Purpose: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) exert a significant influence on various cancer-related processes through their intricate interactions with RNAs. Among these, lncRNA ZFAS1 has been implicated in oncogenic roles in multiple cancer types. Nevertheless, the intricate biological significance and underlying mechanism of ZFAS1 in the initiation and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain largely unexplored.
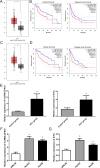
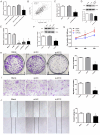
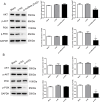
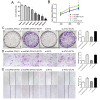
Methods: Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA) database revealed a notable upregulation of lncRNA ZFAS1 in HCC tissues. To explore its function, we investigated colony formation and performed CCK-8 assays to gauge cellular proliferation and wound healing, Transwell assays to assess cellular migration, and an in vivo study employing a nude mouse model to scrutinize tumor growth and metastasis. Luciferase reporter assay was used to confirm the implicated interactions. Rescue experiments were conducted to unravel the plausible mechanism underlying the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway by lncRNAs ZFAS1 and ATIC.
Results: ZFAS1 and ATIC were significantly upregulated in the HCC tissues and cells. ZFAS1 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and migration. We observed a direct interaction between the lncRNA ZFAS1 and ATIC. ATIC knockdown also suppressed cell proliferation and migration. SC79, an activator of AKT, partially restores the effects of lncRNA ZFAS1/ATIC knockdown on cell proliferation and migration. Knockdown of lncRNA ZFAS1/ATIC inhibited tumor growth and lung metastasis in vivo.
Conclusion: Overall, lncRNA ZFAS1 regulates ATIC transcription and contributes to the growth and migration of HCC cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: ATIC; Hepatocellular carcinoma; PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; SC79; lncRNA ZFAS1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abozeid F et al (2022) Diagnostic value of long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 as a potential biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Med J Viral Hepat 6:18–24. 10.21608/mjvh.2022.234479
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

