GGA1 interacts with the endosomal Na+/H+ exchanger NHE6 governing localization to the endosome compartment
- PMID: 39002678
- PMCID: PMC11375261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107552
GGA1 interacts with the endosomal Na+/H+ exchanger NHE6 governing localization to the endosome compartment
Abstract
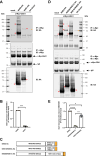
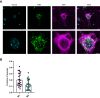
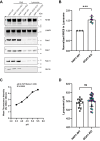
Mutations in the endosomal Na+/H+ exchanger 6 (NHE6) cause Christianson syndrome, an X-linked neurological disorder. NHE6 functions in regulation of endosome acidification and maturation in neurons. Using yeast two-hybrid screening with the NHE6 carboxyl terminus as bait, we identify Golgi-associated, gamma adaptin ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) binding protein 1 (GGA1) as an interacting partner for NHE6. We corroborated the NHE6-GGA1 interaction using: coimmunoprecipitation; overexpressed constructs in mammalian cells; and coimmunoprecipitation of endogenously expressed GGA1 and NHE6 from neuroblastoma cells, as well as from the mouse brain. We demonstrate that GGA1 interacts with organellar NHEs (NHE6, NHE7, and NHE9) and that there is significantly less interaction with cell-surface localized NHEs (NHE1 and NHE5). By constructing hybrid NHE1/NHE6 exchangers, we demonstrate the cytoplasmic tail of NHE6 interacts most strongly with GGA1. We demonstrate the colocalization of NHE6 and GGA1 in cultured, primary hippocampal neurons, using super-resolution microscopy. We test the hypothesis that the interaction of NHE6 and GGA1 functions in the localization of NHE6 to the endosome compartment. Using subcellular fractionation experiments, we show that NHE6 is mislocalized in GGA1 KO cells, wherein we find less NHE6 in endosomes, but more NHE6 transport to lysosomes, and more Golgi retention of NHE6, with increased exocytosis to the surface plasma membrane. Consistent with NHE6 mislocalization, and Golgi retention, we find the intraluminal pH in Golgi to be alkalinized in GGA1-null cells. Our study demonstrates a new interaction between NHE6 and GGA1 which functions in the localization of this intracellular NHE to the endosome compartment.
Keywords: ARF binding protein 1 (GGA1); Christianson syndrome (CS); Golgi; Golgi-associated; Na+/H+ exchanger 6 (NHE6); endosome; exchangers; gamma adaptin ear containing; intracellular trafficking; lysosome.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures






Update of
-
GGA1 interacts with the endosomal Na+/H+ Exchanger NHE6 governing localization to the endosome compartment.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 9:2023.11.08.565997. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.08.565997. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107552. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107552. PMID: 37986849 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Christianson A.L., Stevenson R.E., van der Meyden C.H., Pelser J., Theron F.W., van Rensburg P.L., et al. X linked severe mental retardation, craniofacial dysmorphology, epilepsy, ophthalmoplegia, and cerebellar atrophy in a large South African kindred is localised to Xq24-q27. J. Med. Genet. 1999;36:759–766. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

