Natural compounds-based nanomedicines for cancer treatment: Future directions and challenges
- PMID: 39003425
- PMCID: PMC11385056
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-024-01649-z
Natural compounds-based nanomedicines for cancer treatment: Future directions and challenges
Abstract
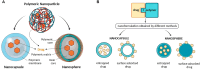
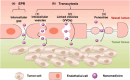
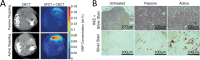
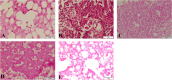
Several efforts have been extensively accomplished for the amelioration of the cancer treatments using different types of new drugs and less invasives therapies in comparison with the traditional therapeutic modalities, which are widely associated with numerous drawbacks, such as drug resistance, non-selectivity and high costs, restraining their clinical response. The application of natural compounds for the prevention and treatment of different cancer cells has attracted significant attention from the pharmaceuticals and scientific communities over the past decades. Although the use of nanotechnology in cancer therapy is still in the preliminary stages, the application of nanotherapeutics has demonstrated to decrease the various limitations related to the use of natural compounds, such as physical/chemical instability, poor aqueous solubility, and low bioavailability. Despite the nanotechnology has emerged as a promise to improve the bioavailability of the natural compounds, there are still limited clinical trials performed for their application with various challenges required for the pre-clinical and clinical trials, such as production at an industrial level, assurance of nanotherapeutics long-term stability, physiological barriers and safety and regulatory issues. This review highlights the most recent advances in the nanocarriers for natural compounds secreted from plants, bacteria, fungi, and marine organisms, as well as their role on cell signaling pathways for anticancer treatments. Additionally, the clinical status and the main challenges regarding the natural compounds loaded in nanocarriers for clinical applications were also discussed.
Keywords: Biological compounds; Cancer cells; Clinical trials; Drug delivery and targeting; Nanocarriers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








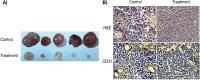



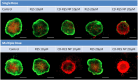



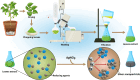

References
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer. World Health Organization. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer. Accessed Apr 2024.
-
- Matthews HK, Bertoli C, De Bruin RAM. Cell cycle control in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23:74–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

