Lower energy intake associated with higher risk of cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease patients on a low-protein diets
- PMID: 39004744
- PMCID: PMC11247864
- DOI: 10.1186/s12937-024-00980-y
Lower energy intake associated with higher risk of cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease patients on a low-protein diets
Abstract
Objective: An increasing number of studies shown that inadequate energy intake causes an increase in adverse incidents in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients on low-protein diets (LPD). The study aimed to investigate the relationship between energy intake and cardiovascular mortality in CKD patients on a LPD.
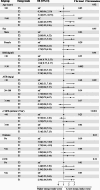
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study, a total of 4264 CKD patients were enrolled from the NHANES database between 2009 and 2018. Restricted cubic spline plots and Cox regression analysis were used to analyze the association between energy intake and cardiovascular mortality in CKD patients on a LPD. Additionally, a nomogram was constructed to estimate cardiovascular survival in CKD patients on a LPD.
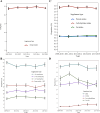
Results: Among CKD patients on a LPD in the United States, 90.05% had an energy intake of less than 25 kcal/kg/day, compared to 36.94% in CKD patients on a non-LPD. Energy intake and cardiovascular mortality showed a linear relationship in CKD patients on a LPD, while a 'U-shaped' relationship was observed in CKD patients on a non-LPD. Multifactorial Cox regression models revealed that for Per-standard deviation (Per-SD) decrement in energy intake, the risk of cardiovascular mortality increased by 41% (HR: 1.41, 95% CI: 1.12, 1.77; P = 0.004) in CKD patients on a LPD. The concordance index of the nomogram was 0.79 (95% CI, 0.75, 0.83).
Conclusion: CKD patients, especially those on a LPD, have significantly inadequate energy intake. Lower energy intake is associated with higher cardiovascular mortality in CKD patients on a LPD.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Epidemiology and outcomes; Malnutrition; Mortality risk; Risk factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- SYS23-07/The open funding of sichuan provincial key laboratory of development and regeneration
- CYZYB22-04/The funding of Chengdu medical college
- JYZK202201/The funding of department of clinical medicine, Chengdu medical college
- CYZYB22-02/The Science and technology fund of Chengdu Medical College
- KY2022QN0309/The research fund of Sichuan Medical and Health Care Promotion institute
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

