Exploring the antitumor potential of novel quinoline derivatives via tubulin polymerization inhibition in breast cancer; design, synthesis and molecular docking
- PMID: 39005243
- PMCID: PMC11240139
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra04371e
Exploring the antitumor potential of novel quinoline derivatives via tubulin polymerization inhibition in breast cancer; design, synthesis and molecular docking
Abstract
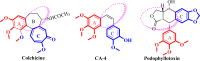
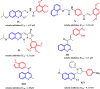
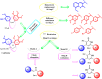
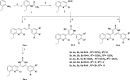
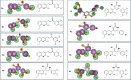
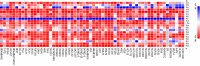
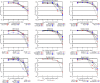
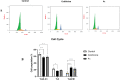
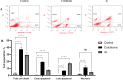
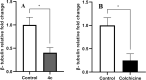
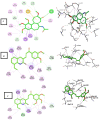
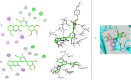
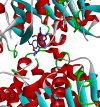
A series of quinoline derivatives was designed and synthesized as novel tubulin inhibitors targeting the colchicine binding site. All the rationalized compounds 3a-e, 4a-e, 5a-e, and 6a-e have been chosen for screening their cytotoxic activity against 60 cell lines by NCI. Compounds 3b, 3c, 4c, 5c and 6c demonstrated the most notable antitumor activity against almost all cell lines. Compound 4c emerged as the most potent compound as an antiproliferative agent. This compound was subsequently chosen for five-dose testing and it exhibited remarkable broad-spectrum efficacy with strong antitumor activity against several cell lines. Compound 4c significantly induced cell cycle arrest in MDA-MB-231 cells at G2 and M phases where the cell population increased dramatically to 22.84% compared to the untreated cells at 10.42%. It also increased the population in MDA-MB-231 cells at both early and late stages of apoptosis. Compound 4c can successfully inhibit tubulin polymerization with an IC50 value of 17 ± 0.3 μM. The β-tubulin mRNA levels were notably reduced in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with compound 4c which is similar to the effect observed with colchicine treatment. Docking studies revealed that compound 4c interacted well with crucial amino acids in the active site.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Malabadi R. B. Sadiya M. Kolkar K. P. Mammadova S. S. Chalannavar R. K. Baijnath H. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2024;11:2502–2539. doi: 10.30574/ijsra.2024.11.1.0315. - DOI
-
- Lu Y. Chen J. Xiao M. Li W. Miller D. D. Pharm. Res. 2012;29:2943–2971. doi: 10.1007/s11095-012-0828-z.An. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

