Analytical quality by design approach to develop an eco-friendly RP-HPLC method for estimation of irbesartan in chitosan polymeric nanoparticles: forced degradation studies and assessment of in vitro release mathematical modelling
- PMID: 39005249
- PMCID: PMC11243759
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra03952a
Analytical quality by design approach to develop an eco-friendly RP-HPLC method for estimation of irbesartan in chitosan polymeric nanoparticles: forced degradation studies and assessment of in vitro release mathematical modelling
Abstract
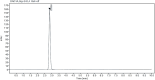
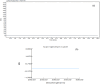
Irbesartan is an angiotensin converting enzyme blocker, primarily utilized for the management of hypertension and the mitigation of diabetic nephropathy progression. The present study introduces rapid, robust and environmentally sustainable reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) validated under the analytical quality by design (AQbD) framework according to ICH guidelines. Utilizing a central composite design, the method's systemic optimization was achieved, ensuring reproducibility and accuracy. Chromatographic separation was accomplished utilizing an ethanol and sodium acetate buffer (60 : 40 v/v) isocratic mobile phase system on a zorbax sb C18 column, with a flow rate of at 0.6 mL min-1. Studies on forced degradation outlined stability of irbesartan and its degradation processes, enhancing our understanding of its chemical robustness under varied conditions. Complementing the green chemistry paradigm, the method's environmental impact was critically assessed, affirming its alignment with sustainability objectives. The validated method proved pivotal in determining the percent entrapment and loading efficiency of the formulated nanoparticles and holds potential for application in biological matrices. Furthermore, the encapsulation of IRB within chitosan nanoparticles was explored to assess release kinetics and enhance bioavailability. This study not only advances the analytical sciences by merging eco-friendly practices with method development but also broadens the applicative landscape of HPLC methodologies in drug delivery research.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Brunner H. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997;10:311S–317S. - PubMed
-
- Pouleur H. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997;10:318S–324S. - PubMed
-
- Hedaya M. A. Helmy S. A. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2015;36:216–231. - PubMed
-
- Boghra R. J. Kothawade P. C. Belgamwar V. S. Nerkar P. P. Tekade A. R. Surana S. J. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011;59:438–441. - PubMed
-
- Chawla G. Bansal A. Acta Pharm. 2008;58(3):257–274. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

