This is a preprint.
Transdiagnostic Neurobiology of Social Cognition and Individual Variability as Measured by Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorders
- PMID: 39005278
- PMCID: PMC11245004
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.02.601737
Transdiagnostic Neurobiology of Social Cognition and Individual Variability as Measured by Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorders
Update in
-
Transdiagnostic Neurobiology of Social Cognition and Individual Variability as Measured by Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in Autism and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2025 Apr 21:S2451-9022(25)00132-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2025.04.004. Online ahead of print. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2025. PMID: 40268245
Abstract
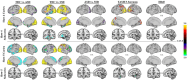
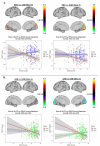
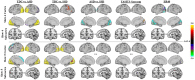
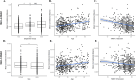
Fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (fALFF) is a validated measure of resting-state spontaneous brain activity. Previous fALFF findings in autism and schizophrenia spectrum disorders (ASDs and SSDs) have been highly heterogeneous. We aimed to use fALFF in a large sample of typically developing control (TDC), ASD and SSD participants to explore group differences and relationships with inter-individual variability of fALFF maps and social cognition. fALFF from 495 participants (185 TDC, 68 ASD, and 242 SSD) was computed using functional magnetic resonance imaging as signal power within two frequency bands (i.e., slow-4 and slow-5), normalized by the power in the remaining frequency spectrum. Permutation analysis of linear models was employed to investigate the relationship of fALFF with diagnostic groups, higher-level social cognition, and lower-level social cognition. Each participant's average distance of fALFF map to all others was defined as a variability score, with higher scores indicating less typical maps. Lower fALFF in the visual and higher fALFF in the frontal regions were found in both SSD and ASD participants compared with TDCs. Limited differences were observed between ASD and SSD participants in the cuneus regions only. Associations between slow-4 fALFF and higher-level social cognitive scores across the whole sample were observed in the lateral occipitotemporal and temporoparietal junction. Individual variability within the ASD and SSD groups was also significantly higher compared with TDC. Similar patterns of fALFF and individual variability in ASD and SSD suggest some common neurobiological deficits across these related heterogeneous conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kahn RS, Sommer IE, Murray RM, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Cannon TD, et al. Schizophrenia (Primer). Nature Reviews: Disease Primers. 2015;1. - PubMed
-
- Yu-Feng Z, Yong H, Chao-Zhe Z, Qing-Jiu C, Man-Qiu S, Meng L, et al. Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain and Development. 2007;29:83–91. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
