This is a preprint.
The Staphylococcus aureus small non-coding RNA IsrR regulates TCA cycle activity and virulence
- PMID: 39005296
- PMCID: PMC11245030
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.03.601953
The Staphylococcus aureus small non-coding RNA IsrR regulates TCA cycle activity and virulence
Update in
-
The Staphylococcus aureus non-coding RNA IsrR regulates TCA cycle activity and virulence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkae1243. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1243. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39704109 Free PMC article.
Abstract
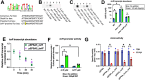
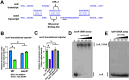
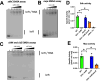
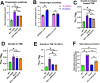
Staphylococcus aureus has evolved mechanisms to cope with low iron (Fe) availability in host tissues. S. aureus uses the ferric uptake transcriptional regulator (Fur) to sense titers of cytosolic Fe. Upon Fe depletion, apo-Fur relieves transcriptional repression of genes utilized for Fe uptake. We demonstrate that an S. aureus Δfur mutant has decreased expression of acnA, which codes for the Fe-dependent enzyme aconitase. Decreased acnA expression prevented the Δfur mutant from growing with amino acids as sole carbon and energy sources. Suppressor analysis determined that a mutation in isrR, which produces a regulatory RNA, permitted growth by decreasing isrR transcription. The decreased AcnA activity of the Δfur mutant was partially relieved by an ΔisrR mutation. Directed mutation of bases predicted to facilitate the interaction between the acnA transcript and IsrR, decreased the ability of IsrR to control acnA expression in vivo and IsrR bound to the acnA transcript in vitro. IsrR also bound to the transcripts coding the alternate TCA cycle proteins sdhC, mqo, citZ, and citM. Whole cell metal analyses suggest that IsrR promotes Fe uptake and increases intracellular Fe not ligated by macromolecules. Lastly, we determined that Fur and IsrR promote infection using murine skin and acute pneumonia models.
Keywords: Fur; IsrR; Staphylococcus aureus; Tsr25; iron.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Staphylococcus aureus non-coding RNA IsrR regulates TCA cycle activity and virulence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkae1243. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1243. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39704109 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the targetome of IsrR, an iron-regulated sRNA controlling the synthesis of iron-containing proteins in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1439352. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1439352. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39035440 Free PMC article.
-
Fpa (YlaN) is an iron(II) binding protein that functions to relieve Fur-mediated repression of gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2024 Nov 13;15(11):e0231024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02310-24. Epub 2024 Oct 23. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39440976 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation by Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) in pathogenic bacteria.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Oct 2;3:59. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00059. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24106689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Sensing by Fe2+ in Bacterial Fur Family Metalloregulators.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Dec 20;29(18):1858-1871. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7359. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28938859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Skaar E.P., Humayun M., Bae T., DeBord K.L. and Schneewind O. (2004) Iron-source preference of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Science, 305, 1626–1628. - PubMed
-
- Torres V.J., Attia A.S., Mason W.J., Hood M.I., Corbin B.D., Beasley F.C., Anderson K.L., Stauff D.L., McDonald W.H., Zimmerman L.J. et al. (2010) Staphylococcus aureus Fur regulates the expression of virulence factors that contribute to the pathogenesis of pneumonia. Infect Immun, 78, 1618–1628. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
