This is a preprint.
Accounting for differences between Infinium MethylationEPIC v2 and v1 in DNA methylation-based tools
- PMID: 39005299
- PMCID: PMC11245009
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.02.600461
Accounting for differences between Infinium MethylationEPIC v2 and v1 in DNA methylation-based tools
Update in
-
Accounting for differences between Infinium MethylationEPIC v2 and v1 in DNA methylation-based tools.Life Sci Alliance. 2025 Jul 8;8(9):e202403155. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403155. Print 2025 Sep. Life Sci Alliance. 2025. PMID: 40628445 Free PMC article.
Abstract
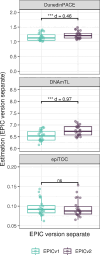
The recently launched Illumina Infinium MethylationEPIC v2.0 (EPICv2), successor of MethylationEPIC v1.0 (EPICv1), retains a majority of probes in EPICv1, while expanding coverage of regulatory elements. The concordance between the two EPIC versions in DNA methylation-based tools has not yet been investigated. To address this, DNA methylation was profiled on both versions using matched blood samples across four cohorts spanning early to late adulthood. High concordance between versions at the array level but variable agreement at the individual probe level was noted. A significant contribution of EPIC version to DNA methylation variation was observed, though it was to a smaller extent compared to sample relatedness and cell type composition. Modest but significant differences in DNA methylation-based estimates between versions were observed, irrespective of the data preprocessing method used. Adjustments for EPIC version or calculation of estimates separately for each version largely mitigated these version-specific discordances. This work emphasizes the importance of accounting for EPIC version differences in research scenarios, especially in meta-analyses and longitudinal studies that require data harmonization across versions.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Epigenetics; Illumina EPIC array; cell type deconvolution; epigenetic clocks; inflammation and lifestyle biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest D.W.B. is listed as an inventor of the Duke University and University of Otago invention DunedinPACE, which is licensed to TruDiagnostic. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Accounting for differences between Infinium MethylationEPIC v2 and v1 in DNA methylation-based tools.Life Sci Alliance. 2025 Jul 8;8(9):e202403155. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403155. Print 2025 Sep. Life Sci Alliance. 2025. PMID: 40628445 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Reminiscence therapy for dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 1;3(3):CD001120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001120.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29493789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
