This is a preprint.
High Throughput Repurposing Screen Reveals Compounds with Activity Against Toxoplasma gondii Bradyzoites
- PMID: 39005312
- PMCID: PMC11244992
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.01.601569
High Throughput Repurposing Screen Reveals Compounds with Activity Against Toxoplasma gondii Bradyzoites
Update in
-
High-Throughput Repurposing Screen Reveals Compounds with Activity against Toxoplasma gondii Bradyzoites.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 14;11(3):600-609. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00689. Epub 2025 Feb 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39933705 Free PMC article.
Abstract
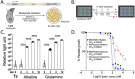
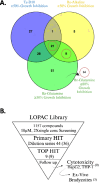
Toxoplasma gondii causes widespread chronic infections that are not cured by current treatments due to inability to affect semi-dormant bradyzoite stages within tissue cysts. To identify compounds to eliminate chronic infection, we developed a HTS using a recently characterized strain of T. gondii that undergoes efficient conversion to bradyzoites in intro. Stage-specific expression of luciferase was used to selectively monitor growth inhibition of bradyzoites by the Library of Pharmacological Active Compounds, consisting of 1,280 drug-like compounds. We identified 44 compounds with >50% inhibitory effects against bradyzoites, including new highly potent compounds, several of which have precedent for antimicrobial activity. Subsequent characterization of the compound Sanguinarine sulfate revealed potent and rapid killing against in vitro produced bradyzoites and bradyzoites harvested from chronically infected mice. These findings provide a platform for expanded screening and identify promising compounds for further preclinical development against T. gondii bradyzoites responsible for chronic infection.
Keywords: High throughput screening; chronic infection; toxoplasmosis.
Figures


References
-
- Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2010. 313 p.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
