This is a preprint.
Promoted Read-through and Mutation Against Pseudouridine-CMC by an Evolved Reverse Transcriptase
- PMID: 39005393
- PMCID: PMC11244976
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.07.03.601893
Promoted Read-through and Mutation Against Pseudouridine-CMC by an Evolved Reverse Transcriptase
Update in
-
Promoted read-through and mutation against pseudouridine-CMC by an evolved reverse transcriptase.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 11;8(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07467-4. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39799263 Free PMC article.
Abstract
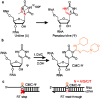
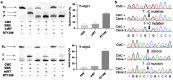
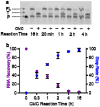
Pseudouridine (Ψ) is an abundant RNA chemical modification that can play critical roles in the biological functions of RNA, and RNA-therapeutic applications. Current Ψ detection methods are limited in identifying Ψs at base-resolution in U-rich sequence contexts, where Ψ occurs frequently. The N-cyclohexyl N'-(2-morpholinoethyl)carbodiimide (CMC) can selectively label Ψ in RNA by forming the CMC-Ψ adduct. Here we report that an evolved reverse transcriptase ("RT-1306") shows promoted read-through and mutation against the CMC-Ψ. The mutation signature can resolve the occurrence of Ψs within UU-containing sequences. We developed "Mut-Ψ-seq" utilizing CMC and RT-1306 for transcriptome-wide mapping of Ψ at base-resolution. The mutation signatures robustly identify reported Ψs in human rRNAs via the ROC analysis, and elongated CMC reaction duration increases the detection sensitivity of Ψ. We report a high-confidence list of Ψ sites in polyA-enriched RNAs from HEK-293T cells identified by orthogonal chemical treatments (CMC and bisulfite). The mutation signatures resolve the position of Ψ in UU-containing sequences, revealing diverse occurrence of Ψs in such sequences. This work provides new methods and datasets for biological research of Ψ, and demonstrates the potential of combining the reverse transcriptase engineering and selective chemical labeling to expand the toolkit for RNA chemical modifications studies.
Keywords: carbodiimide-RNA reaction; high-throughput sequencing; human transcriptome; pseudouridine; reverse transcriptase signature.
Figures


References
-
- Davis F. F., Allen F. W., J Biol Chem 1957, 227, 907–915. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
