The consumption of lard oil during pregnancy and postpartum periods has negative effects on cognitive function by altering the fatty acid profile and activating neuroinflammation via calcium signaling pathway in the maternal mice brain
- PMID: 39005495
- PMCID: PMC11246016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100797
The consumption of lard oil during pregnancy and postpartum periods has negative effects on cognitive function by altering the fatty acid profile and activating neuroinflammation via calcium signaling pathway in the maternal mice brain
Abstract
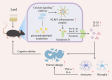
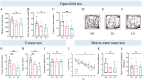
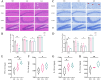
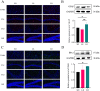
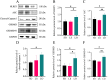
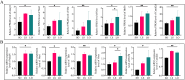
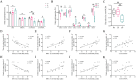
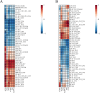
It has been suggested that dietary intake of lipids and fatty acids may influence cognitive function, however, the effect of lard intake during pregnancy and postpartum periods on cognitive function of mother remains to be elucidated. We investigated the effect and mechanism of consuming soybean oil (SO), the mixed oil of lard and soybean oil at the ratio of 1:1 (LS) and lard oil (LO) during the pregnancy and postpartum periods on cognitive function of the maternal mice. All pregnant C57BL/6JNifdc mice were fed with soybean oil diet during day 0-10 (the day when vaginal plugs appeared in female mice was recorded as day 0), and then randomly assigned to SO, LS and LO groups (n = 10) from day 11 to day 44. The time in center zone and the number of times to enter in center zone were significantly higher in the SO group than in the LO group detected by the open-field test. The levels of neuroglial cells, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome complex and pyroptosis related proteins in brain of the LO group were significantly higher than those in the SO group. RNA-sequencing results showed that the calcium signaling pathway related genes in brain, including Adcy8, Ntsr1, Trhr, Oxtr, Htr5b and Camk2d levels significantly higher in the LO group than in the SO group. Lipidomic analysis indicated that PG 18:2_18:2, PG 20:5_22:6, and CL 12:0_16:0_22:3_22:5 of glycerophospholipid metabolism in brain significantly connected with Htr5b of calcium signaling pathway. In conclusion, the intake of lard during the pregnancy and postpartum periods is detrimental to the cognitive function of maternal mice, which probably due to changes in the composition of fatty acid in the brain, thereby activating neuroinflammation via calcium signaling pathway in brain.
Keywords: Lard; Neuroinflammation; Omega-3 fatty acid; Postpartum cognitive function.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Aziz N.U.A., Chiroma S.M., Moklas M.A.M., Adenan M.I., Ismail A., Basir R., Ali R.M., Bin Baharuldin M.T.H. Menhaden fish oil attenuates postpartum depression in rat model via inhibition of NLRP3-inflammasome driven inflammatory pathway. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine. 2021;11(5):419–426. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.02.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

