Stenotrophomonas maltophilia-associated odontogenic cerebral abscess in an immunocompetent patient: A case report
- PMID: 39005575
- PMCID: PMC11239531
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.9168
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia-associated odontogenic cerebral abscess in an immunocompetent patient: A case report
Abstract
Key clinical message: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia can cause rare odontogenic brain abscesses in immunocompetent patients, highlighting the importance of considering uncommon pathogens in central nervous system infections. With only three reported cases of cerebral abscesses and one pituitary abscess caused by this microorganism, tailored diagnostic methods and individualized treatment regimens are crucial for accurate management.
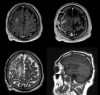
Abstract: Brain abscesses present diagnostic and therapeutic challenges, with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections being exceptionally rare in the central nervous system. We present a case of odontogenic brain abscesses caused by S. maltophilia in an immunocompetent patient, highlighting the rarity and complexity of such infections. A 66-year-old male presented with spatial-temporal disorientation and left-sided weakness. Radiological investigations revealed an expansive lesion in the right posterior frontal region. A craniotomy and drainage were performed, identifying S. maltophilia in the purulent material. The patient responded well to tailored antibiotic therapy. S. maltophilia-related central nervous system infections are infrequent, emphasizing the need for a heightened clinical suspicion in atypical cases. This case contributes to the literature, emphasizing the importance of a multidisciplinary approach for successful diagnosis and management.
Keywords: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; brain abscess; immunocompetent; multidisciplinary approach; odontogenic infection.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

