The Time to Negative Conversion among Adult COVID-19 Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis Admitted at the Philippine General Hospital - A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 39005616
- PMCID: PMC11240000
- DOI: 10.47895/amp.vi0.6460
The Time to Negative Conversion among Adult COVID-19 Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis Admitted at the Philippine General Hospital - A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Objectives: In the Philippines, patients on chronic hemodialysis with COVID-19 remain admitted in hospitals despite clinical recovery because most free-standing dialysis units require proof of negative conversion via Reverse Transcriptase - Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR). This study aims to determine the time to negative conversion of COVID-19 RT-PCR testing among adult patients on chronic hemodialysis with COVID-19 admitted at the Philippine General Hospital (PGH) and bring insight in using the symptom or time-based procedure as recommended by local guideline, and ultimately, to ensure delivery of adequate hemodialysis despite being infected with COVID-19, shorten isolation period, and conserve resources especially in resource-limited settings.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study on all adult patients on chronic hemodialysis who were admitted in PGH after the diagnosis of COVID-19 by RT-PCR between March 2020 and February 2021. Descriptive statistics was used in summarizing the data.
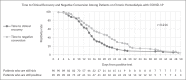
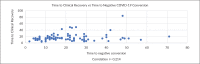
Results: A total of 90 patients on chronic hemodialysis who tested positive for COVID-19 via RT-PCR admitted at PGH were included in the study. Most of these patients had moderate COVID-19 at 53.3%. The median number of days from onset of symptoms to clinical recovery was 14.5 days. The median time to first negative conversion was 18 days. Most of these patients had negative conversion at the second week. The correlation coefficient between time to clinical recovery and negative conversion was 0.214.
Conclusion: Among adult patients on chronic hemodialysis who were admitted in PGH after the diagnosis of COVID-19, the time to negative conversion was longer compared to the time to clinical recovery with a very weak correlation between the two.
Keywords: COVID-19; RT-PCR; hemodialysis.
© 2024 Acta Medica Philippina.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The World Health Organization , Criteria for releasing COVID-19 patients from isolation [Internet]. 2020. [cited 2021 Oct]. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/criteria-for-releasing....
-
- Philippine Society of Nephrology (PSN), Philippine Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (PSMID), Philippine Hospital Infection Control Society (PHICS) , Interim Guidelines in the Prevention and Control of COVID-19 Infection in Hemodialysis Facilities (version2.0) [Internet]. 2020. [cited 2021]. Available from: https://www.psmid.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/PSN-PSMID-PHICS-Interim...
-
- Lee S, Kim T, Lee E, Lee C, Kim H, Rhee H, et al. Clinical course and molecular viral shedding among asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in a community treatment center in the Republic of Korea. JAMA Intern Med. 2020. Nov; 180(11):1447-52. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3862. PMID: 32780793. PMCID: . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources