Association of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome with polycystic ovary syndrome through bidirectional Mendelian randomization
- PMID: 39005659
- PMCID: PMC11239387
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1429783
Association of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome with polycystic ovary syndrome through bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Abstract
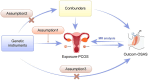
Background: Observational studies have established a link between polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), with obesity being a significant confounding factor that complicates the understanding of causality. This study seeks to clarify the causal relationship by utilizing bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
Methods: A bidirectional MR strategy was implemented to investigate the potential causal relationship between PCOS and OSAS. Instrumental variables (IVs) for PCOS were sourced from a dataset comprising 3,609 cases and 229,788 controls. For OSAS, statistical data were obtained from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) involving 38,998 subjects, alongside a control group of 336,659 individuals. Our MR analysis utilized several methods, including inverse variance weighted (IVW), weighted mode, weighted median, simple mode, and MR-Egger, primarily focusing on the IVW technique. Sensitivity tests were conducted to ensure the robustness of our findings.
Results: Utilizing the IVW method, we identified a notable causal association from OSAS to PCOS, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.463 and a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.086-1.971 (p = 0.012). In the opposite direction, PCOS also appeared to significantly affect OSAS development, indicated by an OR of 1.041 and a 95% CI of 1.012-1.072 (p = 0.006). The MR-Egger intercept test showed no evidence of directional pleiotropy, affirming the credibility of our causal findings (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: This study suggests a bidirectional causal relationship between PCOS and an increased risk of OSAS. These insights could guide future screening and prevention strategies for both conditions.
Keywords: GWAS; Mendelian randomization; OSAS; PCOS; causal inference.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Zhang, Ding and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

