Chidamide represses MYC expression and might improve survival for patients with double expressor lymphoma
- PMID: 39005667
- PMCID: PMC11236771
- DOI: 10.62347/GIIR3351
Chidamide represses MYC expression and might improve survival for patients with double expressor lymphoma
Abstract
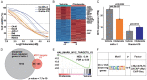
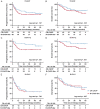
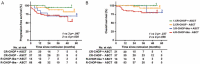
Double expressor lymphoma (DEL), characterized by high expressions of both MYC and BCL-2, displays poor prognosis after current therapies. The HDAC inhibitor chidamide has been approved for treatment of T cell lymphoma, but its efficacy on B cell lymphoma is unclear. Here, by combining inhibition screening and transcriptomic analyses, we found that the sensitivity of B lymphoma cells to chidamide was positively correlated with the expression levels of MYC. Chidamide treatment reduced MYC protein levels and repressed MYC pathway in B lymphoma cells with high MYC expressions. Ectopic expression of MYC in chidamide-insensitive B lymphoma cells increased their response to chidamide. Thus, we proposed that adding chidamide into R-CHOP (CR-CHOP) might be effective for DEL, and retrospectively analyzed 185 DEL patients treated in West China Hospital. 80% of patients showed response to CR-CHOP treatment. In the median follow-up of 42 months, CR-CHOP significantly improve the survival for DEL patients with R-IPI ≤2. Totally 35 patients underwent autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) in remission and demonstrated a trend for better survival. Combining CR-CHOP with ASCT resulted in the most superior PFS and OS above all. For response patients, CR-CHOP reduced relapse with better PFS than R-CHOP-like regimens with or without ASCT. Taken together, our data indicated that chidamide repressed the MYC pathway in B lymphoma and is potentially efficacious to treat DEL.
Keywords: Chidamide; HDAC inhibitor; MYC; double expressor lymphoma; epigenetics.
AJCR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Jiang M, Bennani NN, Feldman AL. Lymphoma classification update: B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017;10:405–415. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Friedberg JW. How I treat double-hit lymphoma. Blood. 2017;130:590–596. - PubMed
-
- Riedell PA, Smith SM. Double hit and double expressors in lymphoma: definition and treatment. Cancer. 2018;124:4622–4632. - PubMed
-
- Green TM, Young KH, Visco C, Xu-Monette ZY, Orazi A, Go RS, Nielsen O, Gadeberg OV, Mourits-Andersen T, Frederiksen M, Pedersen LM, Møller MB. Immunohistochemical double-hit score is a strong predictor of outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:3460–3467. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
