Potential roles of UCH family deubiquitinases in tumorigenesis and chemical inhibitors developed against them
- PMID: 39005671
- PMCID: PMC11236784
- DOI: 10.62347/OEGE2648
Potential roles of UCH family deubiquitinases in tumorigenesis and chemical inhibitors developed against them
Abstract
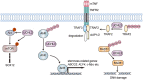
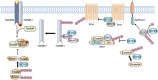
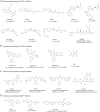
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are a large group of proteases that reverse ubiquitination process and maintain protein homeostasis. The DUBs have been classified into seven subfamilies according to their primary sequence and structural similarity. As a small subfamily of DUBs, the ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs) subfamily only contains four members including UCHL1, UCHL3, UCHL5, and BRCA1-associated protein-1 (BAP1). Despite sharing the deubiquitinase activity with a similar catalysis mechanism, the UCHs exhibit distinctive biological functions which are mainly determined by their specific subcellular localization and partner substrates. Besides, growing evidence indicates that the UCH enzymes are involved in human malignancies. In this review, the structural information and biological functions of the UCHs are briefly described. Meanwhile, the roles of these enzymes in tumorigenesis and the discovered inhibitors against them are also summarized to give an insight into the cancer therapy with the potential alternative strategy.
Keywords: Deubiquitinase; UCH family; cancer; inhibitors.
AJCR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
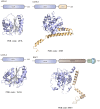
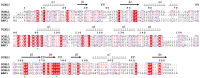
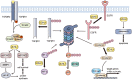
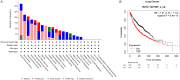


References
-
- Farley AR, Link AJ. Identification and quantification of protein posttranslational modifications. Methods Enzymol. 2009;463:725–763. - PubMed
-
- Montagut AM, Armengol M, de Pablo GG, Estrada-Tejedor R, Borrell JI, Roue G. Recent advances in the pharmacological targeting of ubiquitin-regulating enzymes in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;132:213–229. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
