Recent Trends in Tailoring External Acidity in Zeolites for Catalysis
- PMID: 39005774
- PMCID: PMC11238232
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03899
Recent Trends in Tailoring External Acidity in Zeolites for Catalysis
Abstract
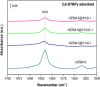
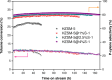
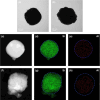
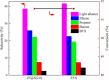
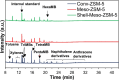
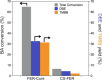
Zeolites are crystalline aluminosilicates with well-defined microporous structures that have found several applications in catalysis. In recent years, great effort has been devoted to defining strategies aimed at tuning structural and acidity properties to improve the catalytic performance of zeolites. Depending on the zeolitic structure, the acid sites located inside the crystals catalyze reactions by exploiting the internal channel shape-selectivity. In contrast, strong acid sites located on the external surface do not offer the possibility to control the size of molecules involved in the reactions. This aspect generally leads to a loss of selectivity toward desired products and to the uncontrolled production of coke. Passivating surface acidity is a promising way to overcome deactivation issues and to enhance the catalytic performance of zeolites. This Mini-Review aims to provide, for the first time, a complete overview of the techniques employed in recent years to neutralize strong external acid sites. Both chemical and liquid vapor deposition of silicates have been widely employed to passivate the external surface acidity of zeolites. In recent years, the epitaxial growth of layers of aluminum-free zeolite, e.g., silicalite-1, over the surface of the acidic zeolite has been proposed as a new approach to neutralize strong external acid sites controlling diffusional phenomena. NH3-TPD, FT-IR, SEM-EDX, and other techniques have been used to provide information about the level of control of the external strong acidity of passivated zeolites. In this Mini-Review, both passivation treatments and characterization techniques are compared and advantages and disadvantages deeply discussed to elucidate the effect of passivation procedures on physical features and especially the catalytic behavior.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures










References
-
- Bellussi G.; Pollesel P. Industrial Applications of Zeolite Catalysis: Production and Uses of Light Olefins. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2005, 158, 1201–1212. 10.1016/S0167-2991(05)80466-5. - DOI
-
- Lakiss L.; Ngoye F.; Canaff C.; Laforge S.; Pouilloux Y.; Qin Z.; Tarighi M.; Thomas K.; Valtchev V.; Vicente A.; Pinard L.; Gilson J.-P.; Fernandez C. On the Remarkable Resistance to Coke Formation of Nanometer-Sized and Hierarchical MFI Zeolites during Ethanol to Hydrocarbons Transformation. J. Catal. 2015, 328, 165–172. 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.12.030. - DOI
-
- Guisnet M.; Costa L.; Ribeiro F. R. Prevention of Zeolite Deactivation by Coking. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 305 (1–2), 69–83. 10.1016/j.molcata.2008.11.012. - DOI
-
- Wei F.-F.; Cui Z.-M.; Meng X.-J.; Cao C.-Y.; Xiao F.-S.; Song W.-G. Origin of the Low Olefin Production over HZSM-22 and HZSM-23 Zeolites: External Acid Sites and Pore Mouth Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2014, 4 (2), 529–534. 10.1021/cs400855p. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
