Long Noncoding RNAs CAT2064 and CAT2042 may Function as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer by Affecting Target MicrorRNAs
- PMID: 39005864
- PMCID: PMC11239640
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-021-00999-6
Long Noncoding RNAs CAT2064 and CAT2042 may Function as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer by Affecting Target MicrorRNAs
Abstract
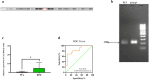
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common cancer in men throughout the world, and the main cause of cancer death. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) act as crucial regulators in many human cancers. In this research, we measured the expression level of novel lncRNAs and their associated micro-RNAs (miRNAs) in PCa. In the present research, three lncRNAs were selected using the Mitranscriptome projec (CAT2064, CAT2042, and CAT2164.2). Samples of prostate tissue (20 PCa, and 20 BPH) and blood (14 PCa, and 14 BPH) were collected and the Real-time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to measure the expression levels of the lncRNAs and their associated miRNAs. Based on our results, CAT2064 was significantly increased and CAT2042 was significantly decreased in human PCa tissue in comparison with BPH tissue. To discriminate PCa from BPH, CAT2064 (P < 0.05; 0.8750 AUC-ROC) showed a better potential as a diagnostic molecular biomarker compared to CAT2042 (P < 0.05; 0.8454 AUC-ROC). Furthermore, RT-qPCR results measured in blood samples from PCa patients showed a higher expression level of CAT2064 (P < 0.0001; AUC-ROC value of 0.8914) in comparison to CAT2042. CAT2064 and CAT2042 showed a positive correlation with the expression of miR-5095 and miR-1273a (r = 0.02885, 0.3202; P = 0.9413, 0.2266, respectively). CAT2064 and CAT2042 also had a negative correlation with miR-1304-3p and miR-1285-5p (r = - 0.3877, - 0.09330; P = 0.15, 0.7311, respectively). Collectively, CAT2064 and CAT2042 and their miRNA targets may constitute a regulatory network in PCa, and could serve as novel biomarkers.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12291-021-00999-6.
Keywords: BPH; Biomarker; PCa; lncRNA; miRNA.
© Association of Clinical Biochemists of India 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Pannek J, Partin A. Prostate-specific Antigen: What's new in Oncology (Williston Park). 1997. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
