Analysis of infrared radiation emitted by moxibustion devices made of different materials using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- PMID: 39005893
- PMCID: PMC11239693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33221
Analysis of infrared radiation emitted by moxibustion devices made of different materials using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
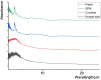
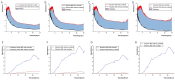
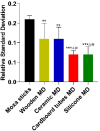
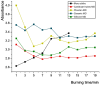
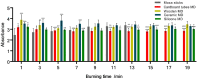
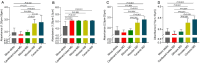
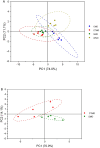
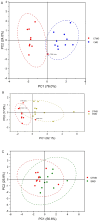
Moxibustion has a long history of use as a traditional Chinese medicine therapy. Infrared radiation is an important and effective factor in moxibustion. Instead of the time-consuming and laborious process of holding moxa sticks in the hand, moxibustion devices are commonly used as moxibustion methods and tools in modern times. With the publication of the international standard of moxibustion devices (ISO18666:2021, Traditional Chinese Medicine - General requirements of moxibustion devices) published, moxibustion devices of various materials are now sold in the pharmacies and online stores. However, the influence of moxibustion devices on the therapeutic effect of moxibustion has not been studied. Therefore, this research was aimed to evaluate the infrared radiation of moxibustion devices, in order to select the moxibustion device that delivered infrared radiation closest to that of moxa stick combustion. The combination of combustion stability and infrared radiation intensity showed that cardboard tubes and silicone were better materials for moxibustion devices. In the mid-far infrared wave band, the moxibustion devices made from cardboard tubes and silica gels can better maintain the thermal effect generated by moxibustion and enable it to be more easily absorbed by the human body. The infrared radiation intensity of the cardboard moxibustion devices increased rapidly and steadily and could be maintained for the longest time. In conclusion, cardboard tubes are the better material for moxibustion devices with respect to infrared radiation.
Keywords: Combustion stability; Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy; Infrared radiation intensity; Integrative medicine; Moxibustion; Principal component analysis; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Rui He and Beixiao Zhao reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100004846Beijing University of Chinese Medicine.This work was supported by 10.13039/501100012166National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2019YFC1711904). If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An infrared radiation study of the biophysical characteristics of traditional moxibustion.Complement Ther Med. 2006 Sep;14(3):213-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2005.09.003. Epub 2005 Dec 15. Complement Ther Med. 2006. PMID: 16911902
-
Characterization of moxa floss combustion by TG/DSC, TG-FTIR and IR.Bioresour Technol. 2019 Sep;288:121516. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121516. Epub 2019 May 19. Bioresour Technol. 2019. PMID: 31176939
-
Moxa sticks: thermal properties and possible implications for clinical trials.Complement Ther Med. 2009 Aug;17(4):243-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2009.01.002. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Complement Ther Med. 2009. PMID: 19632553
-
The mechanism of moxibustion: ancient theory and modern research.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:379291. doi: 10.1155/2013/379291. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 24159344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioengineering assessment of acupuncture, part 8: innovative moxibustion.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;38(2):117-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevbiomedeng.v38.i2.10. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2010. PMID: 20932234 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding factors influencing the adoption of moxibustion techniques by the population: an extended study based on the UTAUT model.Front Public Health. 2025 May 21;13:1508716. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1508716. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40469595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaladat A.M., et al. Similarities and differences between kaiy in Persian medicine and moxibustion in Chinese medicine. J Integr Med. 2023;21(4):354–360. - PubMed
-
- Gaur R. A brief history: traditional Chinese medicinal system. Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine. 2024;10
-
- Zhao Z.W., Fan L. [Comprehensive review and prospect of acupuncture and moxibustion discipline: a review of Discipline History of Acupuncture and Moxibustion in China] Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023;43(5):600–604.
-
- Jinying W., et al. Role and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of acupuncture and moxibustion therapy on pain relief through NOX-ROS-NLRP3 pathway in CCI rats models. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023;50(11):9367–9378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

