Ginkgetin attenuates bone loss in OVX mice by inhibiting the NF-κB/IκBα signaling pathway
- PMID: 39006031
- PMCID: PMC11246017
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17722
Ginkgetin attenuates bone loss in OVX mice by inhibiting the NF-κB/IκBα signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Osteoporosis is a disease associated with bone resorption, characterized primarily by the excessive activation of osteoclasts. Ginkgetin is a compound purified from natural ginkgo leaves which has various biological properties, including anti-inflammation, antioxidant, and anti-tumor effects. This study investigated the bone-protective effects of ginkgetin in ovariectomized (OVX) mice and explored their potential signaling pathway in inhibiting osteoclastogenesis in a mouse model of osteoporosis.
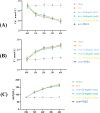
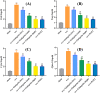
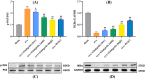
Methods: Biochemical assays were performed to assess the levels of Ca, ALP, and P in the blood. Micro CT scanning was used to evaluate the impact of ginkgetin on bone loss in mice. RT-PCR was employed to detect the expression of osteoclast-related genes (ctsk, c-fos, trap) in their femoral tissue. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was utilized to assess the histopathological changes in femoral tissue due to ginkgetin. The TRAP staining was used to evaluate the impact of ginkgetin osteoclast generation in vivo. Western blot analysis was conducted to investigate the effect of ginkgetin on the expression of p-NF-κB p65 and IκBα proteins in mice.
Results: Our findings indicate that ginkgetin may increase the serum levels of ALP and P, while decreasing the serum level of Ca in OVX mice. H&E staining and micro CT scanning results suggest that ginkgetin can inhibit bone loss in OVX mice. The TRAP staining results showed ginkgetin suppresses the generation of osteoclasts in OVX mice. RT-PCR results demonstrate that ginkgetin downregulate the expression of osteoclast-related genes (ctsk, c-fos, trap) in the femoral tissue of mice, and this effect is dose-dependent. Western blot analysis results reveal that ginkgetin can inhibit the expression of p-NF-κB p65 and IκBα proteins in mice.
Conclusion: Ginkgetin can impact osteoclast formation and activation in OVX mice by inhibiting the NF-κB/IκBα signaling pathway, thereby attenuating bone loss in mice.
Keywords: Ginkgetin; NF-κB; Osteoclasts; Osteoporosis.
© 2024 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Alharbi KS, Fuloria NK, Fuloria S, Rahman SB, Al-Malki WH, Javed Shaikh MA, Thangavelu L, Singh SK, Rama Raju Allam VS, Jha NK, Chellappan DK, Dua K, Gupta G. Nuclear factor-kappa B and its role in inflammatory lung disease. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2021;345(Suppl 3):109568. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109568. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brinkley TE, Lovato JF, Arnold AM, Furberg CD, Kuller LH, Burke GL, Nahin RL, Lopez OL, Yasar S, Williamson JD, Ginkgo Evaluation of Memory (GEM) Study Investigators Effect of ginkgo biloba on blood pressure and incidence of hypertension in elderly men and women. American Journal of Hypertension. 2010;23(5):528–533. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2010.14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

