Integrative analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome provides insights into polysaccharide accumulation in Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce rhizome
- PMID: 39006032
- PMCID: PMC11243984
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17699
Integrative analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome provides insights into polysaccharide accumulation in Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce rhizome
Abstract
Background: Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce is a traditional Chinese herb that is widely cultivated in China. Polysaccharides are the major bioactive components in rhizome of P. odoratum and have many important biological functions.
Methods: To better understand the regulatory mechanisms of polysaccharide accumulation in P. odoratum rhizomes, the rhizomes of two P. odoratum cultivars 'Y10' and 'Y11' with distinct differences in polysaccharide content were used for transcriptome and metabolome analyses, and the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) were identified.
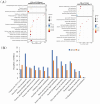
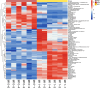
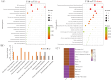
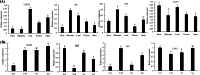
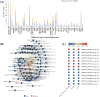
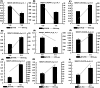
Results: A total of 14,194 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, of which 6,689 DEGs were down-regulated in 'Y10' compared with those in 'Y11'. KEGG enrichment analysis of the down-regulated DEGs revealed a significant enrichment of 'starch and sucrose metabolism', and 'amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism'. Meanwhile, 80 differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) were detected, of which 52 were significantly up-regulated in 'Y11' compared to those in 'Y10'. The up-regulated DAMs were significantly enriched in 'tropane, piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis', 'pentose phosphate pathway' and 'ABC transporters'. The integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis have revealed that four DAMs, glucose, beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate, maltose and 3-beta-D-galactosyl-sn-glycerol were significantly enriched for polysaccharide accumulation, which may be regulated by 17 DEGs, including UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (UGP2), hexokinase (HK), sucrose synthase (SUS), and UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase (UGDH). Furthermore, 8 DEGs (sacA, HK, scrK, GPI) were identified as candidate genes for the accumulation of glucose and beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate in the proposed polysaccharide biosynthetic pathways, and these two metabolites were significantly associated with the expression levels of 13 transcription factors including C3H, FAR1, bHLH and ERF. This study provided comprehensive information on polysaccharide accumulation and laid the foundation for elucidating the molecular mechanisms of medicinal quality formation in P. odoratum rhizomes.
Keywords: Metabolome; Polygonatum Odoratum (Mill.) Druce; Polysaccharide accumulation; Transcriptome.
©2024 Pan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Chen LS, Xu SW, Liu YJ, Zu YH, Zhang FY, Du LJ, Chen J, Li L, Wang K, Wang YT, Chen SJ, Chen ZP, Du XF. Identification of key gene networks controlling polysaccharide accumulation in different tissues of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua by integrating metabolic phenotypes and gene expression profiles. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2022;13:1012231. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1012231. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2020. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission; pp. 88–89.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

