Identification of Hypoxia and Mitochondrial-related Gene Signature and Prediction of Prognostic Model in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39006078
- PMCID: PMC11242342
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.97374
Identification of Hypoxia and Mitochondrial-related Gene Signature and Prediction of Prognostic Model in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
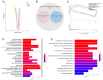
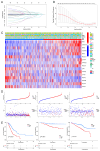
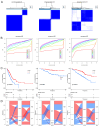
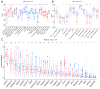
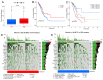
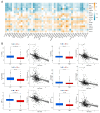
Background: The correlation between hypoxia and tumor development is widely acknowledged. Meanwhile, the foremost organelle affected by hypoxia is mitochondria. This study aims to determine whether they possess prognostic characteristics in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). For this purpose, a bioinformatics analysis was conducted to assess hypoxia and mitochondrial scores related genes, resulting in the successful establishment of a prognostic model. Methods: Using the single sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis algorithm, the hypoxia and mitochondrial scores were computed. Differential expression analysis and weighted correlation network analysis were employed to identify genes associated with hypoxia and mitochondrial scores. Prognosis-related genes were obtained through univariate Cox regression, followed by the establishment of a prognostic model using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator Cox regression. Two independent validation datasets were utilized to verify the accuracy of the prognostic model using receiver operating characteristic and calibration curves. Additionally, a nomogram was employed to illustrate the clinical significance of this study. Results: 318 differentially expressed genes associated with hypoxia and mitochondrial scores were identified for the construction of a prognostic model. The prognostic model based on 16 genes, including PKM, S100A16, RRAS, TUBA4A, PKP3, KCTD12, LPGAT1, ITPRID2, MZT2A, LIFR, PTPRM, LATS2, PDIK1L, GORAB, PCDH7, and CPED1, demonstrates good predictive accuracy for LUAD prognosis. Furthermore, tumor microenvironments analysis and drug sensitivity analysis indicate an association between risk scores and certain immune cells, and a higher risk scores suggesting improved chemotherapy efficacy. Conclusion: The research established a prognostic model consisting of 16 genes, and a nomogram was developed to accurately predict the prognosis of LUAD patients. These findings may contribute to guiding clinical decision-making and treatment selection for patients with LUAD, ultimately leading to improved treatment outcomes.
Keywords: hypoxia; immune; lung adenocarcinoma; mitochondrial; prognosis..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Harris AL. Hypoxia-a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:38–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

