Comparative study of the severity of Covid-19 infection between female and male patients
- PMID: 39006174
- PMCID: PMC11238169
- DOI: 10.60787/nmj-v65i1-451
Comparative study of the severity of Covid-19 infection between female and male patients
Abstract
Background: Different studies have identified the prognostic factors of COVID-19 infection. These studies have revealed that COVID-19 infection is more severe in males than in females. The aim of our study was to compare the severity of COVID-19 infection between males and females in terms of clinical, biological, radiological, and evolutionary aspects.
Methodology: This is a cross-sectional observational study conducted in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection over a 6-month period from 1 August 2021 to 1 February 2022.
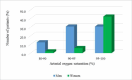
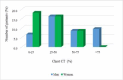
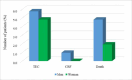
Results: The comparison of clinical, biological, radiological, and evolutionary severity factors of covid-19 infection between the two sexes revealed that this infection was more severe in males. Statistically significant differences were noted for the rate of high dimers (p =0.01) and for lung involvement greater than 25% on chest CT (Computed tomography) (p =0.008).
Conclusion: The severity of covid-19 infection in men is due to biological differences between men and women in the renin-angiotensin system, the immune system, genetics, and sex hormones. Further research into the pathophysiological mechanisms behind this finding is needed.
Keywords: Biological Differences.; COVID-19; Gender; Severity.
Copyright © 2024 Nigerian Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gralinski LE, Menachery VD. Return of the coronavirus: 2019-ncov. Viruses 2020; 2(2):135. doi: 10.3390/v12020135. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Waechter C. Manifestations cliniques et paracliniques de la COVID-19, diagnostic virologique [Clinical and paraclinical features of COVID-19, virological diagnosis]. Npg. 2021. Oct;21(125):297–303.
-
- Zhonghua L, Xing B, Xue ZZ. Epidemiology Working Group for NCIP Epidemic Response, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China Front. Mol. Biosci 2020; 41(2):145–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources