The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and osteoarthritis: evidence from an observational and Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39006235
- PMCID: PMC11239388
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1425327
The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and osteoarthritis: evidence from an observational and Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Objectives: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are common comorbidities that significantly impact individuals' quality of life. However, the relationship between OSA and OA remains unclear. This study aims to explore the connection between OSA and OA and evaluate causality using Mendelian randomization (MR).
Methods: A total of 12,454 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2009-2012) were included. OSA participants were identified based on self-reported interviews. The association between OA and OSA was assessed through multivariable logistic regression analysis. A two-sample MR was employed to investigate the relationship between OSA and OA, specifically hip OA and knee OA, utilizing the inverse variance-weighted (IVW) approach.
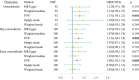
Results: Based on the observational study, individuals with OSA exhibited a higher risk of OA (OR = 1.67, 95% CI = 1.40-1.98). IVW demonstrated that the risk of OA (OR = 1.13, 95% CI: 1.05-1.21, p = 0.001), hip OA (OR = 1.11, 95% CI: 1.04-1.18, p = 0.002), and knee OA (OR = 1.08, 95% CI: 1.02-1.14, p = 0.005) was significantly associated with OSA. Reverse MR analyses indicated no effect of OA on OSA. Additionally, body mass index (BMI) was found to mediate 36.9% (95% CI, 4.64-73.2%, p = 0.026) of the OSA effects on OA risk.
Conclusion: The cross-sectional observational analysis unveiled noteworthy associations between OSA and OA. Meanwhile, findings from the MR study provide support for a causal role.
Keywords: BMI—body mass index; Mendelian randomization; NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey); obstructive sleep apnea; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Lv, Jin, Lv, Zhu, Wang, Zhang, Tu, Chen and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


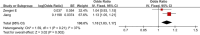

Similar articles
-
Unraveling the relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and osteoarthritis: A multivariate mendelian randomization highlighting the role of BMI as a confounding factor.Exp Gerontol. 2025 Jan;199:112657. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112657. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Exp Gerontol. 2025. PMID: 39672284
-
Osteoarthritis and hypertension: observational and Mendelian randomization analyses.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Apr 17;26(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03321-w. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38632649 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of causality between obstructive sleep apnea and interstitial lung disease: Insights from two-sample mendelian randomization.Respir Med. 2025 Aug;244:108157. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2025.108157. Epub 2025 May 16. Respir Med. 2025. PMID: 40383162
-
The causality between leisure sedentary behaviors, physical activity and obstructive sleep apnea: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 21;12:1425060. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1425060. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38975351 Free PMC article.
-
The common link between sleep apnea syndrome and osteoarthritis: a literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 21;11:1401309. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1401309. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39234045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-level phenotypic models of cardiovascular disease and obstructive sleep apnea comorbidities: A longitudinal Wisconsin sleep cohort study.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 15;20(7):e0327977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327977. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40663595 Free PMC article.
-
Association between body roundness index and obstructive sleep apnea: a cross-sectional study from the NHANES (2005-2008 to 2015-2020).BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 30;25(1):666. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05957-9. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40307762 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

