Risk factors for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and construction of a nomogram predictive model
- PMID: 39006265
- PMCID: PMC11236668
- DOI: 10.62347/DHAJ4799
Risk factors for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and construction of a nomogram predictive model
Abstract
Background: To analyze the risk factors for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) and to construct a predictive nomogram model.
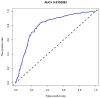
Methods: In this retrospective study, 312 participants were enrolled, including 164 BPPV patients and 148 healthy subjects without BPPV. Risk predictors for BPPV were identified using univariate and multivariate analyses, and a clinical nomogram was constructed. The predictive accuracy was assessed by unadjusted concordance index (C-index) and calibration plot.
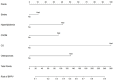
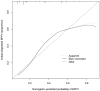
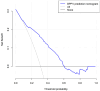
Results: Univariate and multivariate regression analysis identified stroke (95% CI, 0.575-5.954; P=0.022), hyperlipidemia (95% CI, 0.471-4.647; P=0.003), chronic suppurative otitis media (95% CI, 1.222-45.528; P=0.005), cervical spondylosis (95% CI, 1.232-3.017; P=0.005), and osteoporosis (95% CI, 1.130-3.071; P=0.001) were the independent risk factors for BPPV. These risk factors were used to construct a clinical predictive nomogram. The regression equation was: logit (P) = -6.820 + 0.450 * stroke + hyperlipidemia * 0.312 + chronic suppurative otitis media * 0.499 + cervical spondylosis * 0.916 + osteoporosis * 0.628. The calibration curves demonstrated excellent accuracy of the predictive nomogram. Decision curve analysis showed that the predictive model is clinically applicable when the threshold probability was between 20% and 60%.
Conclusions: Stroke, hyperlipidemia, chronic suppurative otitis media, cervical spondylosis and osteoporosis are independent risk predictors for BPPV. The developed nomogram is useful in predicting the risk of BPPV.
Keywords: Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; nomogram; predictive effect; risk factors.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Kim JS, Zee DS. Clinical practice. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1138–1147. - PubMed
-
- Imai T, Inohara H. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2022;49:737–747. - PubMed
-
- Alla S, Rao MY, Aslam SM. Clinical profiles of elderly patients presenting with persistent dizziness. J Natl Med Assoc. 2020;112:362–373. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
