PD-1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone: efficacy and prognostic analysis in recurrent metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 39006268
- PMCID: PMC11236648
- DOI: 10.62347/PAAP2909
PD-1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone: efficacy and prognostic analysis in recurrent metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the prognostic value of combining PD-1 inhibitors (toripalimab or karelizumab) with chemotherapy for treating recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (R/M NPC).
Methods: This study retrospectively analyzed 142 patients with R/M NPC diagnosed from January 2018 to January 2022. Patients were divided into PD-1 inhibitor combined with chemotherapy group (53 patients) and chemotherapy alone group (89 patients) according to the treatment regimen. Objective remission rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), and treatment-related toxicity were evaluated in both groups.
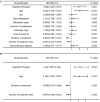
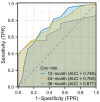
Results: The overall response rate (P=0.006) and objective remission rate (ORR) (P=0.002) were significantly higher in the combination chemotherapy group than in the chemotherapy-alone group. The incidences of hypothyroidism (P<0.001) and reactive capillary hyperplasia (P<0.001) were significantly higher in the combination chemotherapy group than in the chemotherapy-alone group. Cox regression analysis showed that treatment regimen (P<0.001), age (P<0.001), treatment duration (P=0.002), and number of treatment lines (P=0.034) were independent prognostic factors affecting patients' PFS. The prediction model constructed based on these prognostic factors had high accuracy in predicting 1-year and 2-year PFS (AUC 0.746 and 0.760, respectively).
Conclusion: PD-1 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy significantly improved the ORR and median PFS of patients with R/M NPC, while maintaining a favorable safety profile. Treatment regimen, age, number of lines and cycle of therapy were important independent prognostic factors for improving PFS in patients.
Keywords: Karelizumab; combination chemotherapy; prediction model; recurrent metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma; toripalimab.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-efficiency and budget-neutral expanded access modeling of the novel PD-1 inhibitor toripalimab versus pembrolizumab in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Med Econ. 2024;27(sup3):1-8. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2024.2331905. Epub 2024 Apr 8. J Med Econ. 2024. PMID: 38488887
-
Development of a prognostic model to identify the metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients who may benefit from chemotherapy combination PD-1 inhibitor.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 17;14:1069010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1069010. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36733479 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, Safety, and Correlative Biomarkers of Toripalimab in Previously Treated Recurrent or Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Phase II Clinical Trial (POLARIS-02).J Clin Oncol. 2021 Mar 1;39(7):704-712. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02712. Epub 2021 Jan 25. J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33492986 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitors in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after failure of platinum-containing regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Nov 30;23(1):1172. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11318-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38037076 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical benefit analysis of PD-1 inhibitors in patients with advanced, recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 24;15:1305810. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1305810. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38327524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Su ZY, Siak PY, Lwin YY, Cheah SC. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current insights and future outlook. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024;3:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Shield KD, Ferlay J, Jemal A, Sankaranarayanan R, Chaturvedi AK, Bray F, Soerjomataram I. The global incidence of lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancers by subsite in 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:51–64. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Pan J, Wang H, Zhao Y, Qu S, Chen N, Chen X, Sun Y, He X, Hu C, Lin L, Yu Q, Wang S, Wang G, Lei F, Wen J, Yang K, Lin Z, Guo Y, Chen S, Huang X, Wu Y, Liang L, Chen C, Bai F, Ma X, Zhang Y, Leaw S, Zhang L, Fang W. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer: a multicenter phase 3 trial (RATIONALE-309) Cancer Cell. 2023;41:1061–1072. e1064. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
