Cloning and characterization of the LvCTL genes encoding C-type lectin from white-leg shrimp ( Litopenaeus vannamei)
- PMID: 39006306
- PMCID: PMC11240081
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.126044.3
Cloning and characterization of the LvCTL genes encoding C-type lectin from white-leg shrimp ( Litopenaeus vannamei)
Abstract
Background: Lectins are carbohydrate-binding protein domains. The C-type lectin designates a requirement for calcium for binding. Proteins contain C-type lectin domains that have a diverse range of functions, including cell-cell adhesion, immune response to pathogens, and apoptosis. This study aimed to investigate the characters of LvCTL-encoding genes from white-leg shrimp ( Litopenaeus vannamei) in Central Vietnam.
Methods: Two PCR products (LvCTL3 and LvCTL4) were cloned and sequenced. The structure and characterization of LvCTL proteins were predicted using bioinformatics tools.
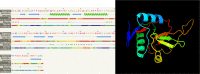
Results: The results showed that the LvCTL3 gene was 444 nucleotides in length and 98.87% similar to the published LvCTL3 gene (accession number: KF156943). The polypeptide sequence had 147 amino acids, which were 97.28% identical to the reference sequence (AGV68681) and the LvCTL4 gene had a length of 417 nucleotides and homology of 99.52% compared to the published gene (KM387560). The deduced polypeptide sequence had 138 amino acids, and was 100% similar to the reference sequence (AKA64754). The LvCTL3 had a molecular weight of 16.91 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) of 4.66, while LvCTL4 had 15.75 and 4.58 kDa, respectively. The structure prediction results showed that LvCTL3 and LvCTL4 had one domain (CTLD), LvCTL3 had two α helices and nine β sheets, and LvCTL4 had two α helices and eight β sheets.
Conclusions: Our results provide essential information for the heterologous expression and biosynthesis production of C-type lectins.
Keywords: C-type lectin; LvCTL genes; gene encoding; white leg shrimp..
Copyright: © 2024 Phuong TV et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures







References
-
- Ha DTT, Tuan LK, Lan PTN, et al. : Cloning and sequencing laccase 3 (folac3) from Fusarium oxysporum. Hue University Journal of Science: Natural Science. 2018;127(1C):1–10. 10.26459/hueuni-jns.v127i1C.4892 - DOI
-
- Junkunlo K, Prachumwat A, Tangprasittipap A, et al. : A novel lectin domain-containing protein (LvCTLD) associated with the response of the whiteleg shrimp Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei to the yellow head virus (YHV). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012;37(3-4):334–341. 10.1016/j.dci.2011.12.010 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

