Decoding connections in the European population: serum uric acid, sex hormone-binding globulin, total testosterone, estradiol, and female infertility - advanced bidirectional and mediative Mendelian randomization
- PMID: 39006368
- PMCID: PMC11239382
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1398600
Decoding connections in the European population: serum uric acid, sex hormone-binding globulin, total testosterone, estradiol, and female infertility - advanced bidirectional and mediative Mendelian randomization
Abstract
Background: Despite observational links between serum uric acid (SUA), sex hormone-related phenotypes, and female infertility, the causality behind these associations remains uncertain.
Objective: This study utilizes Bidirectional Two-Sample and Mediation Mendelian Randomization to explore the causal relationships and mediation effects of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), total testosterone (TT), and estradiol on these associations.
Methods: We analyzed single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with SUA and sex hormone levels using data from large-scale GWAS of European populations. Female infertility data were sourced from 6,481 cases and 75,450 controls in the FinnGen Consortium. We employed methods including Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW), Weighted Median, and MR-Egger regression to assess causality.
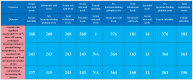
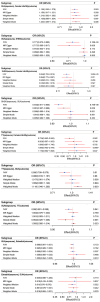
Results: We found that elevated SUA levels causally increase the risk of female infertility (IVW OR: 1.13, P=0.047). Elevated SUA levels significantly decrease SHBG levels (β=-0.261; P=2.177e-04), with SHBG mediating 27.93% of the effect of SUA on infertility (OR=0.854; 95%CI, 0.793-0.920; P=2.853e-05). Additionally, elevated TT levels, which were associated with decreased SUA levels (β=-0.127), showed an indirect effect on infertility mediated by SUA (β=-0.0187; 95% CI, -0.041 to -0.003; P=0.046).
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate causal links between high SUA and increased risk of female infertility mediated by hormonal factors such as SHBG and TT. These insights suggest new avenues for infertility treatment and highlight the need for further research into these mechanisms.
Keywords: European; endocrinology; female infertility; genome wide association; mediated Mendelian randomization; metabolism.
Copyright © 2024 Tan, Shen, Huang, Li, Ding, Sun, Hong, Yang, He, Zhu and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

