Augmented Cornus officinalis Levels in Liuwei Dihuang Decoction Inhibits Nucleus Pulposus Cell Pyroptosis to Enhance Therapeutic Efficacy Against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- PMID: 39006498
- PMCID: PMC11246628
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S465690
Augmented Cornus officinalis Levels in Liuwei Dihuang Decoction Inhibits Nucleus Pulposus Cell Pyroptosis to Enhance Therapeutic Efficacy Against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Abstract
Background: Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration (IVDD) is highly prevalent among the elderly population and stands as a leading cause of low back pain. Our prior studies have highlighted the therapeutic potential of Liuwei Dihuang decoction (LWDHD) and its component Cornus officinalis (CO)-derived compounds in alleviating IVDD and osteoarthritis, suggesting beneficial effects of CO in treating degenerative osteoarthropathies. However, uncertainty remains regarding the optimal CO dosage within LWDHD and its potential mechanism for effectively treating IVDD.
Objective: To ascertain the optimal dosage of CO within LWDHD for enhancing its therapeutic efficacy in treating IVDD, through a comparison of its effects across varied dosages using a mouse IVDD model.
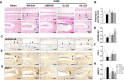
Methods: Eight-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were subjected to a lumbar spine instability surgery to induce an IVDD model and received a modified LWDHD formulation containing varied dosages of CO (original dose of CO, or 5- or 10-time dose of CO (referred to as 1 × CO, 5 × CO, and 10 × CO)) for 8 weeks. The therapeutic efficacy on IVDD was evaluated through changes in lumbar spine function, histopathological morphology, extracellular matrix metabolism, nucleus pulposus cell viability, sensory nerve ingrowth, and nucleus pulposus (NP) cell pyroptosis.
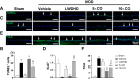
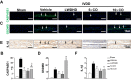
Results: Augmenting CO levels in LWDHD led to a dose-dependent increase in the levels of CO-sourced active compounds in the plasma of mice. The modified LWDHD formulations, particularly the 5 × CO, exhibited a favorable pharmacological effect on lumbar function, structural integrity, ECM composition, NP cell viability, and sensory nerve ingrowth. Importantly, all 3 formulations notably mitigated NP cell pyroptosis by activating NRF2/KEAP1 pathway, with the 5 × CO formulation exhibiting superior efficacy. Additionally, a comprehensive score analysis indicated that 5 × CO formulation achieved the highest score.
Conclusion: These data underscore that elevating the dosage of CO to a specific threshold can enhance the effectiveness of LWDHD in treating IVDD.
Keywords: Cornus officinalis; intervertebral disc degeneration; liuwei dihuang decoction; nucleus pulposus cell; pyroptosis.
© 2024 Ge et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
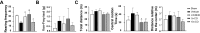


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

