Rituximab in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39006807
- PMCID: PMC11238708
Rituximab in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objective: Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a rare dermatosis of the mucous membrane and/or skin. Employing biologic treatment modalities, specifically rituximab (RTX), have become pivotal measure in treating patients with blistering diseases. This study aims to summarize the current evidence on the safety and efficacy of RTX in EBA.
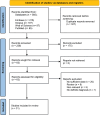
Methods: An extensive search was performed in MEDLINE/PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science databases until the end of August 19th, 2023. Two independent reviewers screened the papers, and collected data. Two hundred thirty-three studies were screened using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses guidelines.
Results: Thirty-one studies were enrolled. The most common reason of RTX administration in patients with EBA was recalcitrant diseases. Clinical response and disease remission was recorded as 92.7 percent (63 patients) and 73.8 percent (45 patients) of the patients, respectively. A relapse rate of 39.5 percent (15 patients) in the mean follow-up of 23.0 months was reported in the studies. Of the patients, 28.2 percent (11 patients) experienced RTX-related side events, mostly mild and transient infusion reactions.
Conclusion: The results of this systematic review demonstrated that RTX is safe and effective in patients with EBA. This biological treatment modality can be routinely used in managing EBA.
Keywords: Autoimmune bullous disease; epidermolysis bullosa acquisita; intravenous immunoglobulin; rituximab; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024. Matrix Medical Communications. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES: The authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Buijsrogge JJ, Diercks GF, Pas HH et al. The many faces of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita after serration pattern analysis by direct immunofluorescence microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165(1):92–98. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources