A review on molecular scissoring with CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technology
- PMID: 39006883
- PMCID: PMC11240166
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfae105
A review on molecular scissoring with CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technology
Abstract
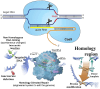
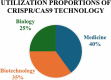
Genome editing is a technology to make specific changes in the DNA of a cell or an organism. It has significantly altered the landscape of life sciences, facilitating the establishment of exceedingly customized genetic modifications. Among various genome editing technologies, the CRISPR/Cas9 system, a specific endonuclease induces a double stranded DNA break and enabling modifications to the genome, has surfaced as a formidable and adaptable instrument. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it not only allows for the manipulation of genomes in model organisms but also holds great potential for revolutionary advances in medicine, particularly in treating genetic diseases. This review paper explores the remarkable journey of CRISPR/Cas9, its natural function, mechanisms, and transformative impact on genome editing and finally the use of artificial intelligence and other intelligent manufacturing tools used. The introduction provides the background on genome editing, emphasizing the emergence and significance of CRISPR/Cas9. Subsequent sections comprehensively elucidate its natural function, disease modeling, agriculture, and biotechnology, address therapeutic applications, and ongoing clinical trials while also discussing prospects and ethical implications. We summarized the key findings, indicating that CRISPR/Cas9 has empowered the creation of disease-specific animal models. This provides invaluable insights into pathogenic mechanisms and opens new avenues for drug discovery, reaffirming the transformative impact of CRISPR/Cas9 on genome editing. Finally we discussed the importance of continued research and collaboration for comprehensive utilization of the inherent capabilities of this molecular precision tool in shaping forthcoming advancements.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; disease modeling; genome editing; therapeutic applications.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Doudna JA, Charpentier E. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science (New York, NY). 2014:346(6213):1258096. - PubMed
-
- Barrangou R, Fremaux C, Deveau H, Richards M, Boyaval P, Moineau S, Romero DA, Horvath P. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science (New York, NY). 2007:315(5819):1709–1712. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources