Screening of a Prognostic Gene Signature for Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Altered Circulating CircRNA Profiles
- PMID: 39006913
- PMCID: PMC11244134
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S466364
Screening of a Prognostic Gene Signature for Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Altered Circulating CircRNA Profiles
Abstract
Background: Relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (R/R-AML) has dismal prognosis due to chemotherapy resistance. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have shown emerging roles in chemotherapy resistance in various cancers including hematologic malignancies. However, the potential roles of circRNAs in AML progression and drug resistance remain largely undetermined.
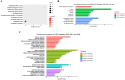
Methods: In this study, circulating circRNAs expression profiles were analyzed among R/R-AML, de novo AML and healthy controls (HC) using a human circRNA Array. Bioinformatic analysis was carried out to explore the differentially expressed circRNAs (DE-circRNAs). GO, KEGG pathway analysis, along with circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network analysis, were conducted to identify the potential biological pathways involved in R/R-AML. Finally, the UALCAN database was used to assess the prognosis of different target DE-circRNAs-related mRNAs.
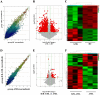
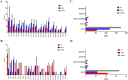
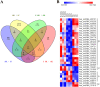
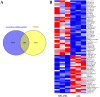
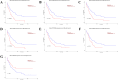
Results: Forty-eight DE-circRNAs were upregulated, whereas twenty-seven DE-circRNAs were downregulated in R/R-AML samples. Up-regulated DE-circRNAs in R/R-AML samples were mainly enrichment in the biological processes and pathways of cell migration, microRNAs in cancers, Rap1 and Ras signaling pathways. Six DE-circRNAs were randomly selected to further explore their relationships with R/R-AML. GO and KEGG pathway analyses of the six candidate DE-circRNAs-related target mRNAs were mainly involved in the regulation of signal transduction and Ras signaling pathway. By overlapping our RNA-sequencing results of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in R/R-AML samples with the candidate DE-circRNAs-predicted target mRNAs, we identified sixty-eight overlapping targeted mRNAs. Using UALCAN database analysis, we identified that AML patients with six upregulated DE-circRNA-related genes (ECE1, PI4K2A, SLC9A6, CCND3, PPP1R16B, and TRIM32) and one downregulated gene DE-circRNA-related genes (ARHGAP10) might have a poor prognosis.
Conclusion: This study revealed the overall alterations of circRNAs in R/R-AML. DE-circRNAs and their related genes might be used as potential early, sensitive and stable biomarkers for AML diagnosis, R/R-AML monitoring, and even as novel treatment targets for R/R-AML.
Keywords: Relapsed/refractory; acute myeloid leukemia; biomarkers; circular RNAs; prognosis.
© 2024 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

