Novel role of Quercetin in ameliorating metabolic syndrome via VDR mediated activation of adiponectin/AdipoR2 signaling
- PMID: 39006943
- PMCID: PMC11246006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101754
Novel role of Quercetin in ameliorating metabolic syndrome via VDR mediated activation of adiponectin/AdipoR2 signaling
Abstract
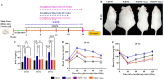
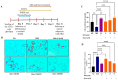
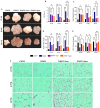
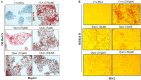
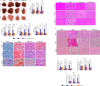
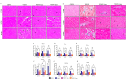
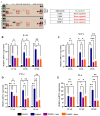
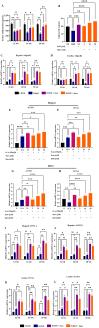
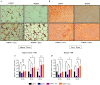
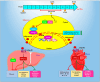
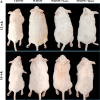
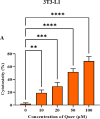
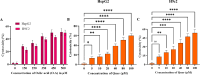
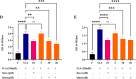
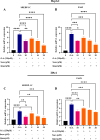
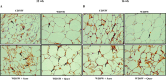
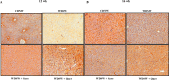
A sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity leads to metabolic syndrome-associated comorbidities involving abdominal obesity, type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidaemia associated Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs), and Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). In this study, we evaluated the novel hepato/cardio/adipo-protective role of Quercetin via Vitamin D Receptor, and elucidated its underlying mechanisms in reducing lipotoxicity, inflammation and fibrosis in high calorie diet induced metabolic syndrome. Male Swiss albino mice were fed with western diet and sugar water for multiple time intervals. Anti-lipotoxicity, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic effect of Quercetin was assessed by Oil Red O, H&E and TMS staining at different time points. The lipid profile, mRNA expression of inflammatory markers (TNF- α, IL-1β, IL-6 and MCP-1), fibrotic markers (α-SMA, COL1A1, COL1A2), adiponectin, AdipoR2, and VDR expression levels were measured from RNA pools of adipose, liver and heart tissues. Also, lipid-lowering and anti-steatohepatitic effects of Quercetin was assessed using mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes, rat H9c2 cardiac cells, and human HepG2 hepatocytes. Our results indicate that, western diet fed mice with Quercetin ameliorated lipid profile and lipotoxicity. Histopathological examination and gene expression data revealed that Quercetin reduced hepatic and cardiac inflammation and fibrosis-associated markers. Interestingly, Quercetin treatment increased the serum levels of adiponectin and mRNA expressions of AdipoR2 and VDR. In-vitro experiments revealed the reduction in lipid accumulation of 3T3-L1 and fatty-acid-treated hepatic and cardiac cells following Quercetin treatment. These findings indicate that Quercetin exhibits a protective role on multiple organs through VDR activation and subsequent Adipo/AdipoR2 signaling in metabolic syndrome associated obesity, hepatic injury, and cardiac dysfunction.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Adiponectin receptor 2; Cardiac fibrosis; Metabolic associated steatohepatitis; Obesity; Quercetin; Vitamin D receptor.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Noubiap J.J., Nansseu J.R., Lontchi-Yimagou E., Nkeck J.R., Nyaga U.F., Ngouo A.T., et al. Global, regional, and country estimates of metabolic syndrome burden in children and adolescents in 2020: a systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health. 2022;6(3):158–170. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00374-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

